 As SLPs we routinely administer a variety of testing batteries in order to assess our students’ speech-language abilities. Grammar, syntax, vocabulary, and sentence formulation get frequent and thorough attention. But how about narrative production? Does it get its fair share of attention when the clinicians are looking to determine the extent of the child’s language deficits? I was so curious about what the clinicians across the country were doing that in 2013, I created a survey and posted a link to it in several SLP-related FB groups. I wanted to find out how many SLPs were performing narrative assessments, in which settings, and with which populations. From those who were performing these assessments, I wanted to know what type of assessments were they using and how they were recording and documenting their findings. Since the purpose of this survey was non-research based (I wasn’t planning on submitting a research manuscript with my findings), I only analyzed the first 100 responses (the rest were very similar in nature) which came my way, in order to get the general flavor of current trends among clinicians, when it came to narrative assessments. Here’s a brief overview of my [limited] findings. Continue reading The Importance of Narrative Assessments in Speech Language Pathology (Revised)
As SLPs we routinely administer a variety of testing batteries in order to assess our students’ speech-language abilities. Grammar, syntax, vocabulary, and sentence formulation get frequent and thorough attention. But how about narrative production? Does it get its fair share of attention when the clinicians are looking to determine the extent of the child’s language deficits? I was so curious about what the clinicians across the country were doing that in 2013, I created a survey and posted a link to it in several SLP-related FB groups. I wanted to find out how many SLPs were performing narrative assessments, in which settings, and with which populations. From those who were performing these assessments, I wanted to know what type of assessments were they using and how they were recording and documenting their findings. Since the purpose of this survey was non-research based (I wasn’t planning on submitting a research manuscript with my findings), I only analyzed the first 100 responses (the rest were very similar in nature) which came my way, in order to get the general flavor of current trends among clinicians, when it came to narrative assessments. Here’s a brief overview of my [limited] findings. Continue reading The Importance of Narrative Assessments in Speech Language Pathology (Revised)
Category: language delay
Early Intervention Evaluations PART IV:Assessing Social Pragmatic Abilities of Children Under 3
 To date, I have written 3 posts on speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age. My first post offered suggestions on what information to include in general speech-language assessments for this age group, my second post specifically discussed assessments of toddlers with suspected motor speech disorders and my third post described what information I tend to include in reports for children ~16-18 months of age.
To date, I have written 3 posts on speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age. My first post offered suggestions on what information to include in general speech-language assessments for this age group, my second post specifically discussed assessments of toddlers with suspected motor speech disorders and my third post described what information I tend to include in reports for children ~16-18 months of age.
Today, I’d like to offer some suggestions on the assessment of social emotional functioning and pragmatics of children, ages 3 and under.
For starters, below is the information I found compiled by a number of researchers on select social pragmatic milestones for the 0-3 age group:
- Peters, Kimberly (2013) Hierarchy of Social/Pragmatic Skills as Related to the Development of Executive Function


- Hutchins & Prelock, (2016) Select Social Cognitive Milestones from the Theory of Mind Atlas

3. Development of Theory of Mind (Westby, 2014)
In my social pragmatic assessments of the 0-3 population, in addition, to the child’s adaptive behavior during the assessment, I also describe the child’s joint attention, social emotional reciprocity, as well as social referencing abilities.
Joint attention is the shared focus of two individuals on an object. Responding to joint attention refers to the child’s ability to follow the direction of the gaze and gestures of others in order to share a common point of reference. Initiating joint attention involves child’s use of gestures and eye contact to direct others’ attention to objects, to events, and to themselves. The function of initiating joint attention is to show or spontaneously seek to share interests or pleasurable experience with others. (Mundy, et al, 2007)
Social emotional reciprocity involves being aware of the emotional and interpersonal cues of others, appropriately interpreting those cues, responding appropriately to what is interpreted as well as being motivated to engage in social interactions with others (LaRocque and Leach,2009).
Social referencing refers to a child’s ability to look at a caregiver’s cues such as facial expressions, body language and tone of voice in an ambiguous situation in order to obtain clarifying information. (Walden & Ogan, 1988)
Here’s a brief excerpt from an evaluation of a child ~18 months of age:
“RA’s joint attention skills, social emotional reciprocity as well as social referencing were judged to be appropriate for his age. For example, when Ms. N let in the family dog from the deck into the assessment room, RA immediately noted that the dog wanted to exit the room and go into the hallway. However, the door leading to the hallway was closed. RA came up to the closed door and attempted to reach the doorknob. When RA realized that he cannot reach to the doorknob to let the dog out, he excitedly vocalized to get Ms. N’s attention, and then indicated to her in gestures that the dog wanted to leave the room.”
 If I happen to know that a child is highly verbal, I may actually include a narrative assessment, when evaluating toddlers in the 2-3 age group. Now, of course, true narratives do not develop in children until they are bit older. However, it is possible to limitedly assess the narrative abilities of verbal children in this age group. According to Hedberg & Westby (1993) typically developing 2-year-old children are at the Heaps Stage of narrative development characterized by
If I happen to know that a child is highly verbal, I may actually include a narrative assessment, when evaluating toddlers in the 2-3 age group. Now, of course, true narratives do not develop in children until they are bit older. However, it is possible to limitedly assess the narrative abilities of verbal children in this age group. According to Hedberg & Westby (1993) typically developing 2-year-old children are at the Heaps Stage of narrative development characterized by
- Storytelling in the form of a collection of unrelated ideas which consist of labeling and describing events
- Frequent switch of topic is evident with lack of central theme and cohesive devices
- The sentences are usually simple declarations which contain repetitive syntax and use of present or present progressive tenses
- In this stage, children possess limited understanding that the character on the next page is still same as on the previous page
In contrast, though typically developing children between 2-3 years of age in the Sequences Stage of narrative development still arbitrarily link story elements together without transitions, they can:
- Label and describe events about a central theme with stories that may contain a central character, topic, or setting
 To illustrate, below is a narrative sample from a typically developing 2-year-old child based on the Mercer Mayer’s classic wordless picture book: “Frog Where Are You?”
To illustrate, below is a narrative sample from a typically developing 2-year-old child based on the Mercer Mayer’s classic wordless picture book: “Frog Where Are You?”
- He put a froggy in there
- He’s sleeping
- Froggy came out
- Where did did froggy go?
- Now the dog fell out
- Then he got him
- You are a silly dog
- And then
- where did froggy go?
- In in there
- Up up into the tree
- Up there an owl
- Froggy
- A reindeer caught him
- Then he dropped him
- Then he went into snow
- And then he cleaned up that
- Then stopped right there and see what wha wha wha what he found
- He found two froggies
- They lived happily ever after
 Of course, a play assessment for this age group is a must. Since, in my first post, I offered a play skills excerpt from one of my early intervention assessments and in my third blog post, I included a link to the Revised Westby Play Scale (Westby, 2000), I will now move on to the description of a few formal instruments I find very useful for this age group.
Of course, a play assessment for this age group is a must. Since, in my first post, I offered a play skills excerpt from one of my early intervention assessments and in my third blog post, I included a link to the Revised Westby Play Scale (Westby, 2000), I will now move on to the description of a few formal instruments I find very useful for this age group.
While some criterion-referenced instruments such as the Rossetti, contain sections on Interaction-Attachment and Pragmatics, there are other assessments which I prefer for evaluating social cognition and pragmatic abilities of toddlers.
 For toddlers 18+months of age, I like using the Language Use Inventory (LUI) (O’Neill, 2009) which is administered in the form of a parental questionnaire that can be completed in approximately 20 minutes. Aimed at identifying children with delay/impairment in pragmatic language development it contains 180 questions and divided into 3 parts and 14 subscales including:
For toddlers 18+months of age, I like using the Language Use Inventory (LUI) (O’Neill, 2009) which is administered in the form of a parental questionnaire that can be completed in approximately 20 minutes. Aimed at identifying children with delay/impairment in pragmatic language development it contains 180 questions and divided into 3 parts and 14 subscales including:
- Communication w/t gestures
- Communication w/t words
- Longer sentences
Therapists can utilize the Automated Score Calculator, which accompanies the LUI in order to generate several pages write up or summarize the main points of the LUI’s findings in their evaluation reports.
Below is an example of a summary I wrote for one of my past clients, 35 months of age.
AN’s ability to use language was assessed via the administration of the Language Use Inventory (LUI). The LUI is a standardized parental questionnaire for children ages 18-47 months aimed at identifying children with delay/impairment in pragmatic language development. Composed of 3 parts and 14 subscales it focuses on how the child communicates with gestures, words and longer sentences.
On the LUI, AN obtained a raw score of 53 and a percentile rank of <1, indicating profoundly impaired performance in the area of language use. While AN scored in the average range in the area of varied word use, deficits were noted with requesting help, word usage for notice, lack of questions and comments regarding self and others, lack of reciprocal word usage in activities with others, humor relatedness, adapting to conversations to others, as well as difficulties with building longer sentences and stories.
Based on above results AN presents with significant social pragmatic language weaknesses characterized by impaired ability to use language for a variety of language functions (initiate, comment, request, etc), lack of reciprocal word usage in activities with others, humor relatedness, lack of conversational abilities, as well as difficulty with spontaneous sentence and story formulation as is appropriate for a child his age. Therapeutic intervention is strongly recommended to improve AN’s social pragmatic abilities.
 In addition to the LUI, I recently discovered the Theory of Mind Inventory-2. The ToMI-2 was developed on a normative sample of children ages 2 – 13 years. For children between 2-3 years of age, it offers a 14 question Toddler Screen (shared here with author’s permission). While due to the recency of my discovery, I have yet to use it on an actual client, I did have fun creating a report with it on a fake client.
In addition to the LUI, I recently discovered the Theory of Mind Inventory-2. The ToMI-2 was developed on a normative sample of children ages 2 – 13 years. For children between 2-3 years of age, it offers a 14 question Toddler Screen (shared here with author’s permission). While due to the recency of my discovery, I have yet to use it on an actual client, I did have fun creating a report with it on a fake client.
First, I filled out the online version of the 14 question Toddler Screen (paper version embedded in the link above for illustration purposes). Typically the parents are asked to place slashes on the form in relevant areas, however, the online version requested that I use numerals to rate skill acquisition, which is what I had done. After I had entered the data, the system generated a relevant report for my imaginary client. In addition to the demographic section, the report generated the following information (below):
- A bar graph of the client’s skills breakdown in the developed, undecided and undeveloped ranges of the early ToM development scale.
- Percentile scores of how the client did in the each of the 14 early ToM measures
- Median percentiles of scores
- Table for treatment planning broken down into strengths and challenges
I find the information provided to me by the Toddler Screen highly useful for assessment and treatment planning purposes and definitely have plans on using this portion of the TOM-2 Inventory as part of my future toddler evaluations.
Of course, the above instruments are only two of many, aimed at assessing social pragmatic abilities of children under 3 years of age, so I’d like to hear from you! What formal and informal instruments are you using to assess social pragmatic abilities of children under 3 years of age? Do you have a favorite one, and if so, why do you like it?
References:
- Hedberg, N.L., & Westby, C.E. (1993). Analyzing story-telling skills: Theory to practice. AZ: Communication Skill Builders.
- Mundy P, Block J, Delgado C, Pomares Y, Vaughan Van Hecke A, Parlade MV. (2007) Individual Differences and the Development of Joint Attention in Infancy. Child Development. 78:938–954
- LaRocque, M., & Leach, D. (2009). Increasing social reciprocity in young children with Autism. Intervention in School and Clinic, 10(5), 1-7.
- O’Neill, D. (2009). Language Use Inventory: An assessment of young children’s pragmatic language development for 18- to 47-month-old children [Manual]. Waterloo, Ontario, Canada Knowledge in Development
- Tomasello, M. (1995). Joint attention as social cognition. In C. Moore, & P. J. Dunham (Eds.), Joint attention: It’s origins and role in development (pp. 103–130). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
- Walden, T., & Ogan, T. (1988). The development of social referencing. Child Development, 59, 1230-1240.
- Westby, C. & Robinson, L. (2014). A developmental perspective for promoting theory of mind. Topics in
Language Disorders, 34(4), 362-383.
Early Intervention Evaluations PART III: Assessing Children Under 2 Years of Age
 In this post, I am continuing my series of articles on speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age. My first installment in this series offered suggestions regarding what information to include in general speech-language assessments for this age group, while my second post specifically discussed assessments of toddlers with suspected motor speech disorders.
In this post, I am continuing my series of articles on speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age. My first installment in this series offered suggestions regarding what information to include in general speech-language assessments for this age group, while my second post specifically discussed assessments of toddlers with suspected motor speech disorders.
Today, I’d like to describe what information I tend to include in reports for children ~16-18 months of age. As I mentioned in my previous posts, the bulk of children I assess under the age of 3, are typically aged 30 months or older. However, a relatively small number of children are brought in for an assessment around an 18-month mark, which is the age group that I would like to discuss today.
Typically, these children are brought in due to a lack of or minimal speech-language production. Interestingly enough, based on the feedback of colleagues, this group is surprisingly hard to report on. While all SLPs will readily state that 18-month-old children are expected to have a verbal vocabulary of at least 50 words and begin to combine them into two-word utterances (e.g., ‘daddy eat’). When prompted: “Well, what else should my child be capable of?” many SLPs draw a blank regarding what else to say to parents on the spot.
 As mentioned in my previous post on assessment of children under 3, the following sections should be an integral part of every early intervention speech-language assessment:
As mentioned in my previous post on assessment of children under 3, the following sections should be an integral part of every early intervention speech-language assessment:
- Background History
- Language Development and Use (Free Questionnaires)
- Adaptive Behavior
- Play Assessment (Westby, 2000) (Westby Play Scale-Revised Link)
- Auditory Function
- Oral Motor Exam
- Feeding and Swallowing
- Vocal Parameters
- Fluency and Resonance
- Articulation and Phonology
- Phonetic inventory
- Phonotactic Repertoire
- Speech intelligibility
- Phonological Processes Analysis (Independent and Relational)
- Receptive Language
- Expressive Language
- Social Emotional Development
- Pragmatic Language
- Impressions
- Recommendations
- Suggested Therapy Goals
- References (if pertinent to a particular report)
In my two previous posts, I’ve also offered examples of select section write-ups (e.g., receptive, expressive phonology, etc.). Below a would like to offer a few more for this age group. Below is an example of a write-up on an 18-month-old bilingual child with a very limited verbal output.
RECEPTIVE LANGUAGE:
L’s receptive language skills were solid at 8 months of age (as per clinical observations and REEL-3 findings) which is significantly below age-expectancy for a child her age (18 months). During the assessment L received credit for appropriately reacting to prohibitive verbalizations (e.g., “No”, “Stop”), attending to speaker when her name was spoken, performing a routine activity upon request (when combined with gestures), looking at familiar object when named, finding the aforementioned familiar object when not in sight, as well as pointing to select body parts on Mrs. L and self (though identification on self was limited). L is also reported to be able to respond to yes/no questions by head nods and shakes.
However, during the assessment L was unable to consistently follow 1 and 2 step directions without gestural cues, understand and perform simple actions per clinician’s request, select objects from a group of 3-5 items given a verbal command, select familiar puzzle pieces from a visual field of 2 choices, understand simple ‘wh questions (e.g., “what?”, “where?”), point to objects or pictures when named, identify simple pictures of objects in book, or display the knowledge and understanding of age appropriate content, function and early concept words (in either Russian or English) as is appropriate for a child her age.
EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE and ARTICULATION
L’s expressive language skills were judged to be solid at 7 months of age (as per clinical observations and REEL-3 findings), which is significantly below age-expectancy for a child her age (18 months). L was observed to spontaneously use proto-imperative gestures (eye gaze, reaching, and leading [by hand]), vocalizations, as well waving for the following language functions: requesting, rejecting, regulating own environment as well as providing closure (waving goodbye).
L’s spontaneous vocalizations consisted primarily of reduplicated babbling (with a limited range of phonemes) which is significantly below age-expectancy for a child her age (see below for developmental norms). During the assessment, L was observed to frequently vocalize “da-da-da”. However, it was unclear whether she was vocalizing to request objects (in Russian “dai” means “give”) due to the fact that she was not observed to consistently vocalize the above solely when requesting items. Additionally, L was not observed to engage in reciprocal babbling or syllable/word imitation during today’s assessment, which is a concern for a child her age. When the examiner attempted to engage L in structured imitation tasks by offering and subsequently denying a toy of interest until L attempted to imitate the desired sound, L became easily frustrated and initiated tantrum behavior. During the assessment, L was not observed to imitate any new sounds trialed with her by the examiner.
During today’s assessment, L’s primary means of communication consisted of eye gaze, reaching, crying, gestures, as well as sound and syllable vocalizations. L’s phonetic inventory consisted of the following consonant sounds: plosives (/p/, /b/ as reported by Mrs. L), alveolars (/t/, /d/ as reported and observed), fricative (/v/ as observed), velar (/g/ as observed), as well as nasal (/n/, and /m/ as observed). L was also observed to produce two vowels /a/ and a pharyngeal /u/. L’s phonotactic repertoire was primarily restricted to reported CV(C-consonant; V-vowel) and VCV syllable shapes, which is significantly reduced for a child her age.
According to developmental norms, a child of L’s age (18 months) is expected to produce a wide variety of consonants (e.g., [b, d, m, n, h, w] in initial and [t, h, s] in final position of words) as well as most vowels. (Robb, & Bleile,(1994); Selby, Robb & Gilbert, 2000). During this time the child’s vocabulary size increases to 50+ words at which point children begin to combine these words to produce simple phrases and sentences (as per Russian and English developmental norms). Additionally, an, 18 months old child is expected to begin monitoring and repairing own utterances, adjusting speech to different listeners, as well as practicing sounds, words, and early sentences. (Clark, adapted by Owens, 2015)
Based on the above guidelines L’s receptive and expressive language, as well as articulation abilities, are judged to be significantly below age expectancy at this time. Speech and language therapy is strongly recommended in order to improve L’s speech and language skills.
Typically when the assessed young children exhibit very limited comprehension and expression, I tend to provide their caregivers with a list of developmental expectations for that specific age group (given the range of a few months) along with recommendations of communication facilitation. Below is an example of such a list, pulled a variety of resources.
 Developmental Milestones expected of a 16-18 months old toddler:
Developmental Milestones expected of a 16-18 months old toddler:
Attention/Gaze:
- Make frequent spontaneous eye contact with adults during interactions
- Turn head to look towards the new voice, when another person begins to talk
- Make 3-point gaze shifts by 1. looking at a toy in hand, 2. then at an adult, 3. then back to the toy
- Make 4-point gaze shifts if more than one person is in the room – by looking from a toy in hand to one person, then the other person, then back to the toy,
- Spontaneously attend to book, activity for 2-3+ minutes without redirection
Reaching and Gestures:
- Show objects in hand to an adult (without actually giving them)
- Push away items that aren’t wanted
- Engage in give and take games when holding objects with an adult
- Imitate simple gestures such as clapping hands or waving bye-bye
- Hand an object to an adult to ask for help with it
- Shake head “no?”
 Play Skills/Routines:
Play Skills/Routines:
- Attempt to actively explore toys (e.g., push or spin parts of toys, turn toys over, roll them back and forth)
- Repeat interesting actions with toys (e.g., make a toy produce an unusual noise, then attempt to make the noise again)
- Imitate simple play activities (adult bangs two blocks together, then child imitates)
- Use objects on daily basis (e.g., when given a spoon or cup the child attempts to feed himself. When putting on clothes the child begins to lift his arms in anticipation of a shirt going on.)
Receptive (Listening Skills):
- Consistently follow 1 and 2 step directions without gestural cues
- Understand and perform simple actions per request (“sit down” or “come here”) without gestures
- Select objects from a group of 3 items given a verbal command
- Select familiar puzzle pieces from a visual field of 2 choices
- Understand simple ‘wh questions (e.g., “what?”, “where?”)
- Point to objects or pictures when named
- Spontaneously and consistently identify simple pictures of objects in book
- Stop momentarily what he is doing if an adult says “no” in a firm voice
- Identify 2-3 common everyday objects or body parts when asked
Expressive (Speaking Skills):
- Produce a wide variety of consonants (e.g., [b, d, m, n, h, w] in initial and [t, h, s] in final position of words) as well as most vowels. (Robb, & Bleile,(1994); Selby, Robb & Gilbert, 2000).
- Have a vocabulary size nearing 50 words (e.g., 35-40)
- Imitate adult words or vocalizations
- Attempt to practice sounds and words (Clark, adapted by Owens, 2015)
- Appropriately label familiar objects (foods, toys, animals)
 Materials to use with the child to promote language and play:
Materials to use with the child to promote language and play:
- Bubbles
- Cause and effect toys
- Toys with a variety of textures (soft toys, plastic toys, cardboard blocks, ridged balls)
- Toys with multiple actions
- Toys with special effects: lights, sounds, movement (push and go vehicles)
- Building and linking toys
- Toys with multiple parts
- Balls, cars and trucks, animals, dolls
- Puzzles
- Pop-up picture books
- Toys the child demonstrates an interest in (parents should advise)
Strategies:
- Reduce distractions (noise, clutter etc)
- Provide one on one interaction in a structured space (e.g., sitting at the play table or sitting on parent’s lap) to improve attention
- Offer favorite activities and toys of interest initially before branching out to new materials
- Offer favorite foods/toys as reinforcers to continue working
- Offer choices of two toys, then remove one toy and focus interaction with one toy of interest
- Try to prolong attention to toy for several minutes at a time
- Change activities frequently, HOWEVER, repeat same activities in cycles over and over again during home practice in order to solidify skills
- Label objects and actions in the child’s immediate environment
- Use brief but loud utterances (2-3 words not more) to gain attention and understanding
- Frequently repeat words in order to ensure understanding of what is said/expected of child
- Use combination of gestures, signs, words, and pictures to teach new concepts
- Do not force child to speak if he doesn’t want to rather attempt to facilitate production of gestures/sounds (e.g., use “hand over hand” to show child the desired gesture such as pointing/waving/motioning in order to reduce his/her frustration
- Use play activities as much as possible to improve child’s ability to follow directions and comprehend language
- Doll House (with Little People)
- Garage
- Farm, etc
 Core vocabulary categories for listening and speaking:
Core vocabulary categories for listening and speaking:
- Favorite and familiar toys and objects
- Names of people in the child’s life as well as his own name
- Pets
- Favorite or familiar foods
- Clothing
- Body parts
- Names of daily activities and actions (go, fall, drink, eat, walk, wash, open)
- Recurrence (more)
- Names of places (bed, outside)
- Safety words (hot, no, stop, dangerous, hurt, don’t touch, yuck, wait)
- Condition words (boo-boo, sick/hurt, mad, happy)
- Early pronouns (me, mine)
- Social words (hi, bye, please, sorry)
- Early concepts: in, off, on, out, big, hot, one, up, down, yucky, wet, all done)
- Yes/no
Select References:
- Owens, R. E. (2015). Language development: An introduction (9th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
- Rescorla, L. (1989). The Language Development Survey: A screening tool for delayed language in toddlers. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 54, 587–599.
- Rescorla, L., Hadicke-Wiley, M., & Escarce, E. (1993). Epidemiological investigation of expressive language delay
at age two. First Language, 13, 5–22. - Robb, M. P., & Bleile, K. M. (1994). Consonant inventories of young children from 8 to 25 months. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics, 8, 295-320.
- Selby, J. C., Robb, M. P., & Gilbert, H. R. (2000). Normal vowel articulations between 15 and 36 months of age. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics, 14, 255-266.
Click HERE for the Early Intervention Evaluations PART IV: Assessing Pragmatic Abilities of Children Under 3
Stay Tuned for the next installment in this series:
- Early Intervention Evaluations PART V: Assessing Feeding and Swallowing in Children Under Two
Improving Executive Function Skills of Language Impaired Students with Hedbanz
 Those of you who have previously read my blog know that I rarely use children’s games to address language goals. However, over the summer I have been working on improving executive function abilities (EFs) of some of the language impaired students on my caseload. As such, I found select children’s games to be highly beneficial for improving language-based executive function abilities.
Those of you who have previously read my blog know that I rarely use children’s games to address language goals. However, over the summer I have been working on improving executive function abilities (EFs) of some of the language impaired students on my caseload. As such, I found select children’s games to be highly beneficial for improving language-based executive function abilities.
For those of you who are only vaguely familiar with this concept, executive functions are higher level cognitive processes involved in the inhibition of thought, action, and emotion, which located in the prefrontal cortex of the frontal lobe of the brain. The development of executive functions begins in early infancy; but it can be easily disrupted by a number of adverse environmental and organic experiences (e.g., psychosocial deprivation, trauma). Furthermore, research in this area indicates that the children with language impairments present with executive function weaknesses which require remediation.
EF components include working memory, inhibitory control, planning, and set-shifting.
- Working memory
- Ability to store and manipulate information in mind over brief periods of time
- Inhibitory control
- Suppressing responses that are not relevant to the task
- Set-shifting
- Ability to shift behavior in response to changes in tasks or environment
Simply put, EFs contribute to the child’s ability to sustain attention, ignore distractions, and succeed in academic settings. By now some of you must be wondering: “So what does Hedbanz have to do with any of it?”
Well, Hedbanz is a quick-paced multiplayer (2-6 people) game of “What Am I?” for children ages 7 and up. Players get 3 chips and wear a “picture card” in their headband. They need to ask questions in rapid succession to figure out what they are. “Am I fruit?” “Am I a dessert?” “Am I sports equipment?” When they figure it out, they get rid of a chip. The first player to get rid of all three chips wins.
The game sounds deceptively simple. Yet if any SLPs or parents have ever played that game with their language impaired students/children as they would be quick to note how extraordinarily difficult it is for the children to figure out what their card is. Interestingly, in my clinical experience, I’ve noticed that it’s not just moderately language impaired children who present with difficulty playing this game. Even my bright, average intelligence teens, who have passed vocabulary and semantic flexibility testing (such as the WORD Test 2-Adolescent or the Vocabulary Awareness subtest of the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy ) significantly struggle with their language organization when playing this game.
So what makes Hedbanz so challenging for language impaired students? Primarily, it’s the involvement and coordination of the multiple executive functions during the game. In order to play Hedbanz effectively and effortlessly, the following EF involvement is needed:
- Task Initiation
- Students with executive function impairments will often “freeze up” and as a result may have difficulty initiating the asking of questions in the game because many will not know what kind of questions to ask, even after extensive explanations and elaborations by the therapist.
- Organization
- Students with executive function impairments will present with difficulty organizing their questions by meaningful categories and as a result will frequently lose their track of thought in the game.
- Working Memory
- This executive function requires the student to keep key information in mind as well as keep track of whatever questions they have already asked.
- Flexible Thinking
- This executive function requires the student to consider a situation from multiple angles in order to figure out the quickest and most effective way of arriving at a solution. During the game, students may present with difficulty flexibly generating enough organizational categories in order to be effective participants.
- Impulse Control
- Many students with difficulties in this area may blurt out an inappropriate category or in an appropriate question without thinking it through first.
- They may also present with difficulty set-shifting. To illustrate, one of my 13-year-old students with ASD, kept repeating the same question when it was his turn, despite the fact that he was informed by myself as well as other players of the answer previously.
- Many students with difficulties in this area may blurt out an inappropriate category or in an appropriate question without thinking it through first.
- Emotional Control
- This executive function will help students with keeping their emotions in check when the game becomes too frustrating. Many students of difficulties in this area will begin reacting behaviorally when things don’t go their way and they are unable to figure out what their card is quickly enough. As a result, they may have difficulty mentally regrouping and reorganizing their questions when something goes wrong in the game.
- Self-Monitoring
- This executive function allows the students to figure out how well or how poorly they are doing in the game. Students with poor insight into own abilities may present with difficulty understanding that they are doing poorly and may require explicit instruction in order to change their question types.
- Planning and Prioritizing
- Students with poor abilities in this area will present with difficulty prioritizing their questions during the game.
Consequently, all of the above executive functions can be addressed via language-based goals. However, before I cover that, I’d like to review some of my session procedures first.
Typically, long before game initiation, I use the cards from the game to prep the students by teaching them how to categorize and classify presented information so they effectively and efficiently play the game.
 Rather than using the “tip cards”, I explain to the students how to categorize information effectively.
Rather than using the “tip cards”, I explain to the students how to categorize information effectively.
This, in turn, becomes a great opportunity for teaching students relevant vocabulary words, which can be extended far beyond playing the game.
I begin the session by explaining to the students that pretty much everything can be roughly divided into two categories animate (living) or inanimate (nonliving) things. I explain that humans, animals, as well as plants belong to the category of living things, while everything else belongs to the category of inanimate objects. I further divide the category of inanimate things into naturally existing and man-made items. I explain to the students that the naturally existing category includes bodies of water, landmarks, as well as things in space (moon, stars, sky, sun, etc.). In contrast, things constructed in factories or made by people would be example of man-made objects (e.g., building, aircraft, etc.)
When I’m confident that the students understand my general explanations, we move on to discuss further refinement of these broad categories. If a student determines that their card belongs to the category of living things, we discuss how from there the student can further determine whether they are an animal, a plant, or a human. If a student determined that their card belongs to the animal category, we discuss how we can narrow down the options of figuring out what animal is depicted on their card by asking questions regarding their habitat (“Am I a jungle animal?”), and classification (“Am I a reptile?”). From there, discussion of attributes prominently comes into play. We discuss shapes, sizes, colors, accessories, etc., until the student is able to confidently figure out which animal is depicted on their card.
In contrast, if the student’s card belongs to the inanimate category of man-made objects, we further subcategorize the information by the object’s location (“Am I found outside or inside?”; “Am I found in ___ room of the house?”, etc.), utility (“Can I be used for ___?”), as well as attributes (e.g., size, shape, color, etc.)
Thus, in addition to improving the students’ semantic flexibility skills (production of definitions, synonyms, attributes, etc.) the game teaches the students to organize and compartmentalize information in order to effectively and efficiently arrive at a conclusion in the most time expedient fashion.
Now, we are ready to discuss what type of EF language-based goals, SLPs can target by simply playing this game.
1. Initiation: Student will initiate questioning during an activity in __ number of instances per 30-minute session given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
2. Planning: Given a specific routine, student will verbally state the order of steps needed to complete it with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
3. Working Memory: Student will repeat clinician provided verbal instructions pertaining to the presented activity, prior to its initiation, with 80% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
4. Flexible Thinking: Following a training by the clinician, student will generate at least __ questions needed for task completion (e.g., winning the game) with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
5. Organization: Student will use predetermined written/visual cues during an activity to assist self with organization of information (e.g., questions to ask) with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
6. Impulse Control: During the presented activity the student will curb blurting out inappropriate responses (by silently counting to 3 prior to providing his response) in __ number of instances per 30 minute session given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
7. Emotional Control: When upset, student will verbalize his/her frustration (vs. behavioral activing out) in __ number of instances per 30 minute session given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
8. Self-Monitoring: Following the completion of an activity (e.g., game) student will provide insight into own strengths and weaknesses during the activity (recap) by verbally naming the instances in which s/he did well, and instances in which s/he struggled with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
There you have it. This one simple game doesn’t just target a plethora of typical expressive language goals. It can effectively target and improve language-based executive function goals as well. Considering the fact that it sells for approximately $12 on Amazon.com, that’s a pretty useful therapy material to have in one’s clinical tool repertoire. For fancier versions, clinicians can use “Jeepers Peepers” photo card sets sold by Super Duper Inc. Strapped for cash, due to highly limited budget? You can find plenty of free materials online if you simply input “Hedbanz cards” in your search query on Google. So have a little fun in therapy, while your students learn something valuable in the process and play Hedbanz today!
Related Smart Speech Therapy Resources:
Early Intervention Evaluations PART I: Assessing 2.5 year olds
 Today, I’d like to talk about speech and language assessments of children under three years of age. Namely, the quality of these assessments. Let me be frank, I am not happy with what I am seeing. Often times, when I receive a speech-language report on a child under three years of age, I am struck by how little functional information it contains about the child’s linguistic strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, conversations with parents often reveal that at best the examiner spent no more than half an hour or so playing with the child and performed very limited functional testing of their actual abilities. Instead, they interviewed the parent and based their report on parental feedback alone. Consequently, parents often end up with a report of very limited value, which does not contain any helpful information on how delayed is the child as compared to peers their age.
Today, I’d like to talk about speech and language assessments of children under three years of age. Namely, the quality of these assessments. Let me be frank, I am not happy with what I am seeing. Often times, when I receive a speech-language report on a child under three years of age, I am struck by how little functional information it contains about the child’s linguistic strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, conversations with parents often reveal that at best the examiner spent no more than half an hour or so playing with the child and performed very limited functional testing of their actual abilities. Instead, they interviewed the parent and based their report on parental feedback alone. Consequently, parents often end up with a report of very limited value, which does not contain any helpful information on how delayed is the child as compared to peers their age.
So today I like to talk about what information should such speech-language reports should contain. For the purpose of this particular post, I will choose a particular developmental age at which children at risk of language delay are often assessed by speech-language pathologists. Below you will find what information I typically like to include in these reports as well as developmental milestones for children 30 months or 2.5 years of age.
 Why 30 months, you may ask? Well, there isn’t really any hard science to it. It’s just that I noticed that a significant percentage of parents who were already worried about their children’s speech-language abilities when they were younger, begin to act upon those worries as the child is nearing 3 years of age and their abilities are not improving or are not commensurate with other peers their age.
Why 30 months, you may ask? Well, there isn’t really any hard science to it. It’s just that I noticed that a significant percentage of parents who were already worried about their children’s speech-language abilities when they were younger, begin to act upon those worries as the child is nearing 3 years of age and their abilities are not improving or are not commensurate with other peers their age.
So here is the information I include in such reports (after I’ve gathered pertinent background information in the form of relevant intakes and questionnaires, of course). Naturally, detailed BACKGROUND HISTORY section is a must! Prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal development should be prominently featured there. All pertinent medical history needs to get documented as well as all of the child’s developmental milestones in the areas of cognition, emotional development, fine and gross motor function, and of course speech and language. Here, I also include a family history of red flags: international or domestic adoption of the child (if relevant) as well as familial speech and language difficulties, intellectual impairment, psychiatric disorders, special education placements, or documented deficits in the areas of literacy (e.g., reading, writing, and spelling). After all, if any of the above issues are present in isolation or in combination, the risk for language and literacy deficits increases exponentially, and services are strongly merited for the child in question.
For bilingual children, the next section will cover LANGUAGE BACKGROUND AND USE. Here, I describe how many and which languages are spoken in the home and how well does the child understand and speak any or all of these languages (as per parental report based on questionnaires).
After that, I move on to describe the child’s ADAPTIVE BEHAVIOR during the assessment. In this section, I cover emotional relatedness, joint attention, social referencing, attention skills, communicative frequency, communicative intent, communicative functions, as well as any and all unusual behaviors noted during the therapy session (e.g., refusal, tantrums, perseverations, echolalia, etc.) Then I move on to PLAY SKILLS. For the purpose of play assessment, I use the Revised Westby Play Scale (Westby, 2000). In this section, I describe where the child is presently with respect to play skills, and where they actually need to be developmentally (excerpt below).
“During today’s assessment, LS’s play skills were judged to be significantly reduced for his age. A child of LS’s age (30 months) is expected to engage in a number of isolated pretend play activities with realistic props to represent daily experiences (playing house) as well as less frequently experienced events (e.g., reenacting a doctor’s visit, etc.) (corresponds to Stage VI on the Westby Play Scale, Revised Westby Play Scale (Westby, 2000)). Contrastingly, LS presented with limited repertoire routines, which were characterized primarily by exploration of toys, such as operating simple cause and effect toys (given modeling) or taking out and then putting back in playhouse toys. LS’s parents confirmed that the above play schemas were representative of play interactions at home as well. Today’s LS’s play skills were judged to be approximately at Stage II (13 – 17 months) on the Westby Play Scale, (Revised Westby Play Scale (Westby, 2000)) which is significantly reduced for a child of LS’s age, since it is almost approximately ±15 months behind his peers. Thus, based on today’s play assessment, LS’s play skills require therapeutic intervention. “
Sections on AUDITORY FUNCTION, PERIPHERAL ORAL MOTOR EXAM, VOCAL PARAMETERS, FLUENCY AND RESONANCE (and if pertinent FEEDING and SWALLOWING follow) (more on that in another post).
Now, it’s finally time to get to the ‘meat and potatoes’ of the report ARTICULATION AND PHONOLOGY as well as RECEPTIVE and EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE (more on PRAGMATIC ASSESSMENT in another post).
First, here’s what I include in the ARTICULATION AND PHONOLOGY section of the report.
- Phonetic inventory: all the sounds the child is currently producing including (short excerpt below):
- Consonants: plosive (/p/, /b/, /m/), alveolar (/t/, /d/), velar (/k/, /g/), glide (/w/), nasal (/n/, /m/) glottal (/h/)
- Vowels and diphthongs: ( /a/, /e/, /i/, /o/, /u/, /ou/, /ai/)
- Phonotactic repertoire: What type of words comprised of how many syllables and which consonant-vowel variations the child is producing (excerpt below)
- LS primarily produced one syllable words consisting of CV (e.g., ke, di), CVC (e.g., boom), VCV (e.g., apo) syllable shapes, which is reduced for a child his age.
- Speech intelligibility in known and unknown contexts
- Phonological processes analysis
Now that I have described what the child is capable of speech-wise, I discuss where the child needs to be developmentally:
“A child of LS’s age (30 months) is expected to produce additional consonants in initial word position (k, l, s, h), some consonants (t, d, m, n, s, z) in final word position (Watson & Scukanec, 1997b), several consonant clusters (pw, bw, -nd, -ts) (Stoel-Gammon, 1987) as well as evidence a more sophisticated syllable shape structure (e.g., CVCVC) Furthermore, a 30 month old child is expected to begin monitoring and repairing own utterances, adjusting speech to different listeners, as well as practicing sounds, words, and early sentences (Clark, adapted by Owens, 1996, p. 386) all of which LS is not performing at this time. Based on above developmental norms, LS’s phonological abilities are judged to be significantly below age-expectancy at this time. Therapy is recommended in order to improve LS’s phonological skills.”
 At this point, I am ready to move on to the language portion of the assessment. Here it is important to note that a number of assessments for toddlers under 3 years of age contain numerous limitations. Some such as REEL-3 or Rosetti (a criterion-referenced vs. normed-referenced instrument) are observational or limitedly interactive in nature, while others such as PLS-5, have a tendency to over inflate scores, resulting in a significant number of children not qualifying for rightfully deserved speech-language therapy services. This is exactly why it’s so important that SLPs have a firm knowledge of developmental milestones! After all, after they finish describing what the child is capable of, they then need to describe what the developmental expectations are for a child this age (excerpts below).
At this point, I am ready to move on to the language portion of the assessment. Here it is important to note that a number of assessments for toddlers under 3 years of age contain numerous limitations. Some such as REEL-3 or Rosetti (a criterion-referenced vs. normed-referenced instrument) are observational or limitedly interactive in nature, while others such as PLS-5, have a tendency to over inflate scores, resulting in a significant number of children not qualifying for rightfully deserved speech-language therapy services. This is exactly why it’s so important that SLPs have a firm knowledge of developmental milestones! After all, after they finish describing what the child is capable of, they then need to describe what the developmental expectations are for a child this age (excerpts below).
RECEPTIVE LANGUAGE
“LS’s receptive language abilities were judged to be scattered between 11-17 months of age (as per clinical observations as well as informal PLS-5 and REEL-3 findings), which is also consistent with his play skills abilities (see above). During the assessment LS was able to appropriately understand prohibitive verbalizations (e.g., “No”, “Stop”), follow simple 1 part directions (when repeated and combined with gestures), selectively attend to speaker when his name was spoken (behavioral), perform a routine activity upon request (when combined with gestures), retrieve familiar objects from nearby (when provided with gestures), identify several major body parts (with prompting) on a doll only, select a familiar object when named given repeated prompting, point to pictures of familiar objects in books when named by adult, as well as respond to yes/no questions by using head shakes and head nods. This is significantly below age-expectancy.
A typically developing child 30 months of age is expected to spontaneously follow (without gestures, cues or prompts) 2+ step directives, follow select commands that require getting objects out of sight, answer simple “wh” questions (what, where, who), understand select spatial concepts, (in, off, out of, etc), understand select pronouns (e.g., me, my, your), identify action words in pictures, understand concept sizes (‘big’, ‘little’), identify simple objects according to their function, identify select clothing items such as shoes, shirt, pants, hat (on self or caregiver) as well as understand names of farm animals, everyday foods, and toys. Therapeutic intervention is recommended in order to increase LS’s receptive language abilities.
EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE:
“During today’s assessment, LS’s expressive language skills were judged to be scattered between 10-15 months of age (as per clinical observations as well as informal PLS-5 and REEL-3 findings). LS was observed to communicate primarily via proto-imperative gestures (requesting and object via eye gaze, reaching) as well as proto-declarative gestures (showing an object via eye gaze, reaching, and pointing). Additionally, LS communicated via vocalizations, head nods, and head shakes. According to parental report, at this time LS’s speaking vocabulary consists of approximately 15-20 words (see word lists below). During the assessment LS was observed to spontaneously produce a number of these words when looking at a picture book, playing with toys, and participating in action based play activities with Mrs. S and clinician. LS was also observed to produce a number of animal sounds when looking at select picture books and puzzles. For therapy planning purposes, it is important to note that LS was observed to imitate more sounds and words, when they were supported by action based play activities (when words and sounds were accompanied by a movement initiated by clinician and then imitated by LS). Today LS was observed to primarily communicate via a very limited number of imitated and spontaneous one word utterances that labeled basic objects and pictures in his environment, which is significantly reduced for his age.
A typically developing child of LS’s chronological age (30 months) is expected to possess a minimum vocabulary of 200+ words (Rescorla, 1989), produce 2-4 word utterance combinations (e.g., noun + verb, verb + noun + location, verb + noun + adjective, etc), in addition to asking 2-3 word questions as well as maintaining a topic for 2+ conversational turns. Therapeutic intervention is recommended in order to increase LS’s expressive language abilities.”
Here you have a few speech-language evaluation excerpts which describe not just what the child is capable of but where the child needs to be developmentally. Now it’s just a matter of summarizing my IMPRESSIONS (child’s strengths and needs), RECOMMENDATIONS as well as SUGGESTED (long and short term) THERAPY GOALS. Now the parents have some understanding regarding their child’s strengths and needs. From here, they can also track their child’s progress in therapy as they now have some idea to what it can be compared to.
 Now I know that many of you will tell me, that this is a ‘perfect world’ evaluation conducted by a private therapist with an unlimited amount of time on her hands. And to some extent, many of you will be right! Yes, such an evaluation was a result of more than 30 minutes spent face-to-face with the child. All in all, it took probably closer to 90 minutes of face to face time to complete it and a few hours to write. And yes, this is a luxury only a few possess and many therapists in the early intervention system lack. But in the long run, such evaluations pay dividends not only, obviously, to your clients but to SLPs who perform them. They enhance and grow your reputation as an evaluating therapist. They even make sense from a business perspective. If you are well-known and highly sought after due to your evaluating expertise, you can expect to be compensated for your time, accordingly. This means that if you decide that your time and expertise are worth private pay only (due to poor insurance reimbursement or low EI rates), you can be sure that parents will learn to appreciate your thoroughness and will choose you over other providers.
Now I know that many of you will tell me, that this is a ‘perfect world’ evaluation conducted by a private therapist with an unlimited amount of time on her hands. And to some extent, many of you will be right! Yes, such an evaluation was a result of more than 30 minutes spent face-to-face with the child. All in all, it took probably closer to 90 minutes of face to face time to complete it and a few hours to write. And yes, this is a luxury only a few possess and many therapists in the early intervention system lack. But in the long run, such evaluations pay dividends not only, obviously, to your clients but to SLPs who perform them. They enhance and grow your reputation as an evaluating therapist. They even make sense from a business perspective. If you are well-known and highly sought after due to your evaluating expertise, you can expect to be compensated for your time, accordingly. This means that if you decide that your time and expertise are worth private pay only (due to poor insurance reimbursement or low EI rates), you can be sure that parents will learn to appreciate your thoroughness and will choose you over other providers.
So, how about it? Can you give it a try? Trust me, it’s worth it!
Selected References:
- Owens, R. E. (1996). Language development: An introduction (4th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
- Rescorla, L. (1989). The Language Development Survey: A screening tool for delayed language in toddlers. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 54, 587–599.
- Selby, J. C., Robb, M. P., & Gilbert, H. R. (2000). Normal vowel articulations between 15 and 36 months of age. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics, 14, 255-266.
- Stoel-Gammon, C. (1987). Phonological skills of 2-year-olds. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 18, 323-329.
- Watson, M. M., & Scukanec, G. P. (1997b). Profiling the phonological abilities of 2-year-olds: A longitudinal investigation. Child Language Teaching and Therapy, 13, 3-14.
For more information on EI Assessments click on any of the below posts:
- Part II: Early Intervention Evaluations PART II: Assessing Suspected Motor Speech Disorders in Children Under 3
- Part III: Early Intervention Evaluations PART III: Assessing Children Under 2 Years of Age
- Part IV: Early Intervention Evaluations PART IV:Assessing Social Pragmatic Abilities of Children Under 3
Treatment of Children with “APD”: What SLPs Need to Know
 In recent years there has been an increase in research on the subject of diagnosis and treatment of Auditory Processing Disorders (APD), formerly known as Central Auditory Processing Disorders or CAPD.
In recent years there has been an increase in research on the subject of diagnosis and treatment of Auditory Processing Disorders (APD), formerly known as Central Auditory Processing Disorders or CAPD.
More and more studies in the fields of audiology and speech-language pathology began confirming the lack of validity of APD as a standalone (or useful) diagnosis. To illustrate, in June 2015, the American Journal of Audiology published an article by David DeBonis entitled: “It Is Time to Rethink Central Auditory Processing Disorder Protocols for School-Aged Children.” In this article, DeBonis pointed out numerous inconsistencies involved in APD testing and concluded that “routine use of APD test protocols cannot be supported” and that [APD] “intervention needs to be contextualized and functional” (DeBonis, 2015, p. 124) Continue reading Treatment of Children with “APD”: What SLPs Need to Know
Is it a Difference or a Disorder? Free Resources for SLPs Working with Bilingual and Multicultural Children
 For bilingual and monolingual SLPs working with bilingual and multicultural children, the question of: “Is it a difference or a disorder?” arises on a daily basis as they attempt to navigate the myriad of difficulties they encounter in their attempts at appropriate diagnosis of speech, language, and literacy disorders.
For bilingual and monolingual SLPs working with bilingual and multicultural children, the question of: “Is it a difference or a disorder?” arises on a daily basis as they attempt to navigate the myriad of difficulties they encounter in their attempts at appropriate diagnosis of speech, language, and literacy disorders.
 For that purpose, I’ve recently created a Checklist for Identification of Speech-Language Disorders in Bilingual and Multicultural Children. Its aim is to assist Speech Language Pathologists (SLPs) and Teachers in the decision-making process of how to appropriately identify bilingual/multicultural children who present with speech-language delay/deficits (vs. a language difference), for the purpose of initiating a formal speech-language-literacy evaluation. The goal is to ensure that educational professionals are appropriately identifying bilingual children for assessment and service provision due to legitimate speech language deficits/concerns, and are not over-identifying students because they speak multiple languages or because they come from low socioeconomic backgrounds. It is very important to understand that true language impairment in bilingual children will be evident in both languages from early childhood onwards, and thus will adversely affect the learning of both languages.
For that purpose, I’ve recently created a Checklist for Identification of Speech-Language Disorders in Bilingual and Multicultural Children. Its aim is to assist Speech Language Pathologists (SLPs) and Teachers in the decision-making process of how to appropriately identify bilingual/multicultural children who present with speech-language delay/deficits (vs. a language difference), for the purpose of initiating a formal speech-language-literacy evaluation. The goal is to ensure that educational professionals are appropriately identifying bilingual children for assessment and service provision due to legitimate speech language deficits/concerns, and are not over-identifying students because they speak multiple languages or because they come from low socioeconomic backgrounds. It is very important to understand that true language impairment in bilingual children will be evident in both languages from early childhood onwards, and thus will adversely affect the learning of both languages.
However, today the aim of today’s post is not on the above product but rather on the FREE free bilingual and multicultural resources available to SLPs online in their quest of differentiating between a language difference from a language disorder in bilingual and multicultural children.
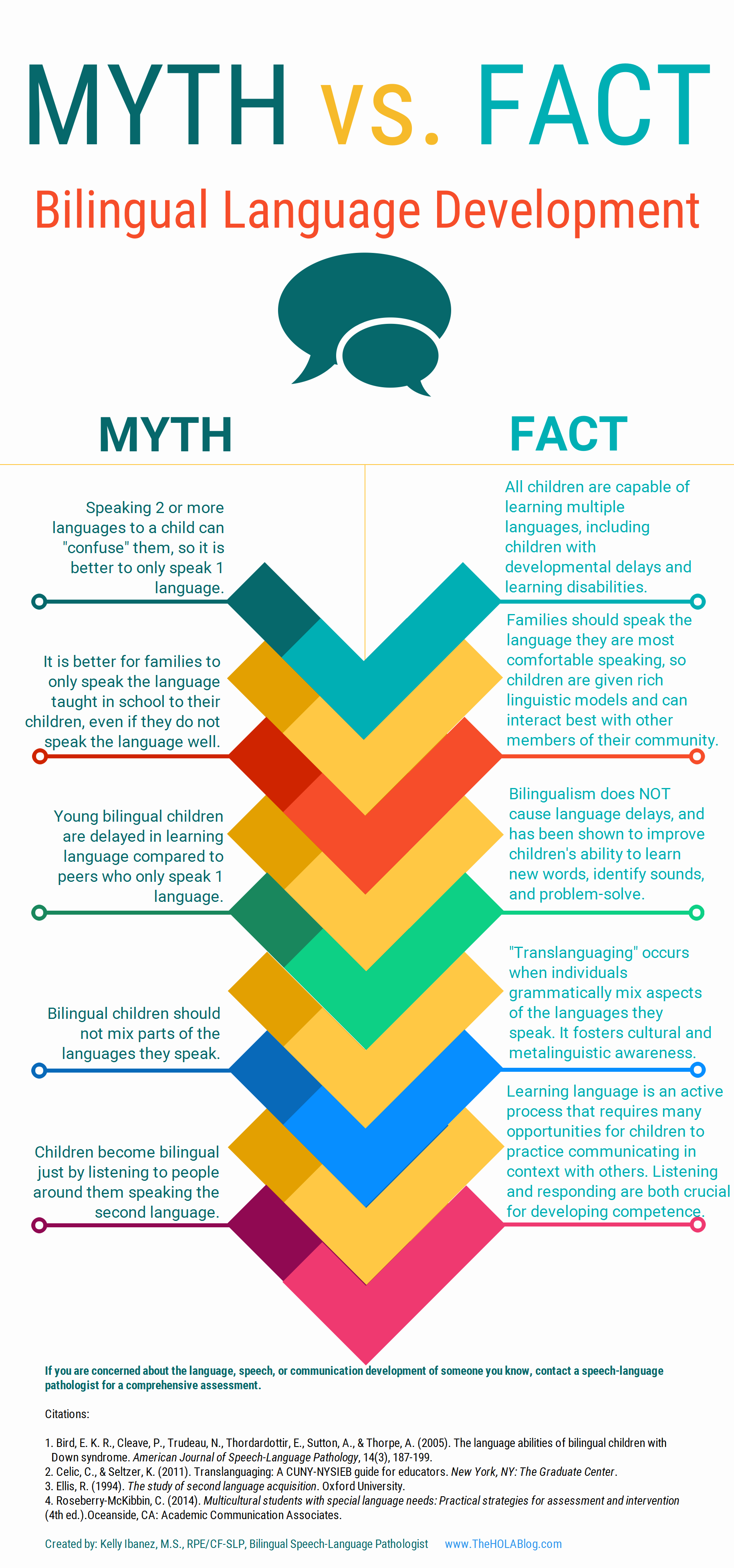 Let’s start with an excellent free infographic entitled from the Hola Blog “Myth vs. Fact: Bilingual Language Development” which was created by Kelly Ibanez, MS CCC-SLP to help dispel bilingual myths and encourage practices that promote multilingualism. Clinicians can download it and refer to it themselves, share it with other health and/or educational professionals as well as show it to parents of their clients.
Let’s start with an excellent free infographic entitled from the Hola Blog “Myth vs. Fact: Bilingual Language Development” which was created by Kelly Ibanez, MS CCC-SLP to help dispel bilingual myths and encourage practices that promote multilingualism. Clinicians can download it and refer to it themselves, share it with other health and/or educational professionals as well as show it to parents of their clients.
Let us now move on to the typical phonological development of English speaking children. After all, in order to compare other languages to English, SLPs need to be well versed in the acquisition of speech sounds in the English language. Children’s speech acquisition, developed by Sharynne McLeod, Ph.D., of Charles Sturt University, is one such resource. It contains a compilation of data on typical speech development for English speaking children, which is organized according to children’s ages to reflect a typical developmental sequence.
 Next up, is a great archive which contains phonetic inventories of the various language spoken around the world for contrastive analysis purposes. The same website also contains a speech accent archive. Native and non-native speakers of English were recorded reading the same English paragraph for teaching and research purposes. It is meant to be used by professionals who are interested in comparing the accents of different English speakers.
Next up, is a great archive which contains phonetic inventories of the various language spoken around the world for contrastive analysis purposes. The same website also contains a speech accent archive. Native and non-native speakers of English were recorded reading the same English paragraph for teaching and research purposes. It is meant to be used by professionals who are interested in comparing the accents of different English speakers.
![]() Now let’s talk about one of my favorite websites, MULTILINGUAL CHILDREN’S SPEECH, also developed by Dr. Mcleod of Charles Stuart University. It contains an AMAZING plethora of resources on bilingual speech development and assessment. To illustrate, its Speech Acquisition Data includes A list of over 200 speech acquisition studies. It also contains a HUGE archive on Speech Assessments in NUMEROUS LANGUAGES as well as select assessment reviews. Finally, the website also lists in detail how aspects of speech (e.g., consonants, vowels, syllables, tones) differ between languages.
Now let’s talk about one of my favorite websites, MULTILINGUAL CHILDREN’S SPEECH, also developed by Dr. Mcleod of Charles Stuart University. It contains an AMAZING plethora of resources on bilingual speech development and assessment. To illustrate, its Speech Acquisition Data includes A list of over 200 speech acquisition studies. It also contains a HUGE archive on Speech Assessments in NUMEROUS LANGUAGES as well as select assessment reviews. Finally, the website also lists in detail how aspects of speech (e.g., consonants, vowels, syllables, tones) differ between languages.
The Leader’s Project Website is another highly informative source of FREE information on bilingual assessments, intervention, and FREE CEUS.
Now, I’d like to list some resources regarding language transfer errors.
This chart from Cengage Learning contains a nice, concise Language Guide to Transfer Errors. While it is aimed at multilingual/ESL writers, the information contained on the site is highly applicable to multilingual speakers as well.
You can also find a bonus transfer chart HERE. It contains information on specific structures such as articles, nouns, verbs, pronouns, adverbs, adjectives, word order, questions, commands, and negatives on pages 1-6 and phonemes on pages 7-8.
A final bonus chart entitled: Teacher’s Resource Guide of Language Transfer Issues for English Language Learners containing information on grammar and phonics for 10 different languages can be found HERE.
Similarly, this 16-page handout: Language Transfers: The Interaction Between English and Students’ Primary Languages also contains information on phonics and grammar transfers for Spanish, Cantonese, Vietnamese, Hmong Korean, and Khmer languages.
 For SLPs working with Russian-speaking children the following links pertinent to assessment, intervention and language transference may be helpful:
For SLPs working with Russian-speaking children the following links pertinent to assessment, intervention and language transference may be helpful:
- Working with Russian-speaking clients: implications for speech-language assessment
- Strategies in the acquisition of segments and syllables in Russian-speaking children
- Language Development of Bilingual Russian/ English Speaking Children Living in the United States: A Review of the Literature
- The acquisition of syllable structure by Russian-speaking children with SLI
To determine information about the children’s language development and language environment, in both their first and second language, visit the CHESL Centre website for The Alberta Language Development Questionnaire and The Alberta Language Environment Questionnaire
There you have it! FREE bilingual/multicultural SLP resources compiled for you conveniently in one place. And since there are much more FREE GEMS online, I’d love it if you guys contributed to and expanded this modest list by posting links and title descriptions in the comments section below for others to benefit from!
Together we can deliver the most up to date evidence-based assessment and intervention to bilingual and multicultural students that we serve! Click HERE to check out the FREE Resources in the SLPs for Evidence-Based Practice Group
Helpful Bilingual Smart Speech Therapy Resources:
- Checklist for Identification of Speech-Language Disorders in Bilingual and Multicultural Children
- Multicultural Assessment Bundle
- Best Practices in Bilingual Literacy Assessments and Interventions
- Dynamic Assessment of Bilingual and Multicultural Learners in Speech-Language Pathology
- Practical Strategies for Monolingual SLPs Assessing and Treating Bilingual Children
- Language Difference vs. Language Disorder: Assessment & Intervention Strategies for SLPs Working with Bilingual Children
- Impact of Cultural and Linguistic Variables On Speech-Language Services
- Assessment of sound and syllable imitation in Russian-speaking infants and toddlers
- Russian Articulation Screener
- Creating Translanguaging Classrooms and Therapy Rooms
A Focus on Literacy
 In recent months, I have been focusing more and more on speaking engagements as well as the development of products with an explicit focus on assessment and intervention of literacy in speech-language pathology. Today I’d like to introduce 4 of my recently developed products pertinent to assessment and treatment of literacy in speech-language pathology.
In recent months, I have been focusing more and more on speaking engagements as well as the development of products with an explicit focus on assessment and intervention of literacy in speech-language pathology. Today I’d like to introduce 4 of my recently developed products pertinent to assessment and treatment of literacy in speech-language pathology.
 First up is the Comprehensive Assessment and Treatment of Literacy Disorders in Speech-Language Pathology
First up is the Comprehensive Assessment and Treatment of Literacy Disorders in Speech-Language Pathology
which describes how speech-language pathologists can effectively assess and treat children with literacy disorders, (reading, spelling, and writing deficits including dyslexia) from preschool through adolescence. It explains the impact of language disorders on literacy development, lists formal and informal assessment instruments and procedures, as well as describes the importance of assessing higher order language skills for literacy purposes. It reviews components of effective reading instruction including phonological awareness, orthographic knowledge, vocabulary awareness, morphological awareness, as well as reading fluency and comprehension. Finally, it provides recommendations on how components of effective reading instruction can be cohesively integrated into speech-language therapy sessions in order to improve literacy abilities of children with language disorders and learning disabilities.
 Next up is a product entitled From Wordless Picture Books to Reading Instruction: Effective Strategies for SLPs Working with Intellectually Impaired Students. This product discusses how to address the development of critical thinking skills through a variety of picture books utilizing the framework outlined in Bloom’s Taxonomy: Cognitive Domain which encompasses the categories of knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation in children with intellectual impairments. It shares a number of similarities with the above product as it also reviews components of effective reading instruction for children with language and intellectual disabilities as well as provides recommendations on how to integrate reading instruction effectively into speech-language therapy sessions.
Next up is a product entitled From Wordless Picture Books to Reading Instruction: Effective Strategies for SLPs Working with Intellectually Impaired Students. This product discusses how to address the development of critical thinking skills through a variety of picture books utilizing the framework outlined in Bloom’s Taxonomy: Cognitive Domain which encompasses the categories of knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation in children with intellectual impairments. It shares a number of similarities with the above product as it also reviews components of effective reading instruction for children with language and intellectual disabilities as well as provides recommendations on how to integrate reading instruction effectively into speech-language therapy sessions.
 The product Improving Critical Thinking Skills via Picture Books in Children with Language Disorders is also available for sale on its own with a focus on only teaching critical thinking skills via the use of picture books.
The product Improving Critical Thinking Skills via Picture Books in Children with Language Disorders is also available for sale on its own with a focus on only teaching critical thinking skills via the use of picture books.
 Finally, my last product Best Practices in Bilingual Literacy Assessments and Interventions focuses on how bilingual speech-language pathologists (SLPs) can effectively assess and intervene with simultaneously bilingual and multicultural children (with stronger academic English language skills) diagnosed with linguistically-based literacy impairments. Topics include components of effective literacy assessments for simultaneously bilingual children (with stronger English abilities), best instructional literacy practices, translanguaging support strategies, critical questions relevant to the provision of effective interventions, as well as use of accommodations, modifications and compensatory strategies for improvement of bilingual students’ performance in social and academic settings.
Finally, my last product Best Practices in Bilingual Literacy Assessments and Interventions focuses on how bilingual speech-language pathologists (SLPs) can effectively assess and intervene with simultaneously bilingual and multicultural children (with stronger academic English language skills) diagnosed with linguistically-based literacy impairments. Topics include components of effective literacy assessments for simultaneously bilingual children (with stronger English abilities), best instructional literacy practices, translanguaging support strategies, critical questions relevant to the provision of effective interventions, as well as use of accommodations, modifications and compensatory strategies for improvement of bilingual students’ performance in social and academic settings.
You can find these and other products in my online store (HERE).
Helpful Smart Speech Therapy Resources:
- Dynamic Assessment of Bilingual and Multicultural Learners in Speech-Language Pathology
- Differential Assessment and Treatment of Processing Disorders in Speech-Language Pathology
- Practical Strategies for Monolingual SLPs Assessing and Treating Bilingual Children
- The Checklists Bundle
- General Assessment and Treatment Start Up Bundle
- Multicultural Assessment Bundle
- Narrative Assessment and Treatment Bundle
- Social Pragmatic Assessment and Treatment Bundle
- Psychiatric Disorders Bundle
Dear SLPs, Here’s What You Need to Know About Internationally Adopted Children
 In the past several years there has been a sharp decline in international adoptions. Whereas in 2004, Americans adopted a record high of 22,989 children from overseas, in 2015, only 5,647 children (a record low in 30 years) were adopted from abroad by American citizens.
In the past several years there has been a sharp decline in international adoptions. Whereas in 2004, Americans adopted a record high of 22,989 children from overseas, in 2015, only 5,647 children (a record low in 30 years) were adopted from abroad by American citizens.

Primary Data Source: Data Source: U.S. State Department Intercountry Adoption Statistics
Secondary Data Source: Why Did International Adoption Suddenly End?
Despite a sharp decline in adoptions many SLPs still frequently continue to receive internationally adopted (IA) children for assessment as well as treatment – immediately post adoption as well as a number of years post-institutionalization.
In the age of social media, it may be very easy to pose questions and receive instantaneous responses on platforms such as Facebook and Twitter with respect to assessment and treatment recommendations. However, it is very important to understand that many SLPs, who lack direct clinical experience in international adoptions may chime in with inappropriate recommendations with respect to the assessment or treatment of these children.
Consequently, it is important to identify reputable sources of information when it comes to speech-language assessment of internationally adopted children.
There are a number of researchers in both US and abroad who specialize in speech-language abilities of Internationally Adopted children. This list includes (but is by far not limited to) the following authors:
- Boris Gindis
- Sharon Glennen
- Deborah Hwa-Froelich
- Kathleen A. Scott
- Jenny A. Roberts
- Karen E. Pollock
- M. Gay Masters
- Monica Dalen
The works of these researchers can be readily accessed in the ASHA Journals or via ResearchGate.
Meanwhile, here are some basic facts regarding internationally adopted children that all SLPs and parents need to know.
Demographics:
- A greater number of older, preschool and school-aged children and fewer number of infants and toddlers are placed for adoption (Selman, 2012).
- Significant increase in special needs adoptions from Eastern European countries (e.g., Ukraine, Kazhakstan, etc.) as well as China. The vast majority of Internationally Adopted children arrive to the United States with significant physical, linguistic, and cognitive disabilities as well as mental health problems. Consequently, it is important for schools to immediately provide the children with a host of services including speech-language therapy, immediately post-arrival.
- It is also important to know that in the vast majority of cases the child’s linguistic, cognitive, or mental health deficits may not be documented in the adoption records due to poor record keeping, lack of access to adequate healthcare or often to ensure their “adoptability”. As such, parental interviews and anecdotal evidence become the primary source of information regarding these children’s social and academic functioning in their respective birth countries.
The question of bilingualism:
- Internationally Adopted children are NOT bilingual children! In fact, the vast majority of internationally adopted children will very rapidly lose their birth language, in a period of 2-3 months post arrival (Gindis, 2005), since they are most often adopted by parents who do not speak the child’s birth language and as such are unable/unwilling to maintain it.
- IA children do not need to be placed in ESL classes since they are not bilingual children. Not only are IA children not bilingual, they are also not ‘truly’ monolingual since their first language is lost rather rapidly, while their second language has been gained minimally at the time of loss.
- IA children need to acquire Cognitive Language Mastery (CLM) which is language needed for formal academic learning. This includes listening, speaking, reading, and writing about subject area content material including analyzing, synthesizing, judging and evaluating presented information. This level of language learning is essential for a child to succeed in school. CLM takes years and years to master, especially because, IA children did not have the same foundation of knowledge and stimulation as bilingual children in their birth countries.
Assessment Parameters:
- IA children’s language abilities should be retested and monitored at regular intervals during the first several years post arrival.
- Glennen (2007) recommends 3 evaluations during the first year post arrival, with annual reevaluations thereafter.
- Hough & Kaczmarek (2011) recommend a reevaluation schedule of 3-4 times a year for a period of two years, post arrival because some IA children continue to present with language-based deficits many years (5+) post-adoption.
- If an SLP speaking the child’s first language is available the window of opportunity to assess in the first language is very limited (~2-3 months at most).
- Similarly, an assessment with an interpreter is recommended immediately post arrival from the birth country for a period of approximately the same time.
- If an SLP speaking the child’s first language is not available English-speaking SLP should consider assessing the child in English between 3-6 months post arrival (depending on the child and the situational constraints) in order to determine the speed with which s/he are acquiring English language abilities
- Children should be demonstrating rapid language gains in the areas of receptive language, vocabulary as well as articulation (Glennen 2007, 2009)
- Dynamic assessment is highly recommended
- It is important to remember that language and literacy deficits are not always very apparent and can manifest during any given period post arrival
To treat or NOT to Treat?
- “Any child with a known history of speech and language delays in the sending country should be considered to have true delays or disorders and should receive speech and language services after adoption.” (Glennen, 2009, p.52)
- IA children with medical diagnoses, which impact their speech language abilities should be assessed and considered for S-L therapy services as well (Ladage, 2009).
Helpful Links:
- Elleseff, T (2013) Changing Trends in International Adoption: Implications for Speech-Language Pathologists. Perspectives on Global Issues in Communication Sciences and Related Disorders, 3: 45-53
- Assessing Behaviorally Impaired Students: Why Background History Matters!
- Dear School Professionals Please Be Aware of This
- What parents need to know about speech-language assessment of older internationally adopted children
- Understanding the risks of social pragmatic deficits in post institutionalized internationally adopted (IA) children
- Understanding the extent of speech and language delays in older internationally adopted children
References:
- Gindis, B. (2005). Cognitive, language, and educational issues of children adopted from overseas orphanages. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 4 (3): 290-315.
- Glennen, S (2009) Speech and language guidelines for children adopted from abroad at older ages. Topics in language Disorders 29, 50-64.
- Ladage, J. S. (2009). Medical Issues in International Adoption and Their Influence on Language Development. Topics in Language Disorders , 29 (1), 6-17.
- Selman P. (2012) Global trends in Intercountry Adoption 2000-2010. New York: National Council for Adoption, 2012.
- Selman P. The global decline of intercountry adoption: What lies ahead?. Social Policy and Society 2012, 11(3), 381-397.
Additional Helpful References:
- Abrines, N., Barcons, N., Brun, C., Marre, D., Sartini, C., & Fumadó, V. (2012). Comparing ADHD symptom levels in children adopted from Eastern Europe and from other regions: discussing possible factors involved. Children and Youth Services Review, 34 (9) 1903-1908.
- Balachova, T et al (2010). Changing physicians’ knowledge, skills and attitudes to prevent FASD in Russia: 800. Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research. 34(6) Sup 2:210A.
- Barcons-Castel, N, Fornieles-Deu,A, & Costas-Moragas, C (2011). International adoption: assessment of adaptive and maladaptive behavior of adopted minors in Spain. The Spanish Journal of Psychology, 14 (1): 123-132.
- Beverly, B., McGuinness, T., & Blanton, D. (2008). Communication challenges for children adopted from the former Soviet Union. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 39, 1-11.
- Cohen, N. & Barwick, M. (1996). Comorbidity of language and social-emotional disorders: comparison of psychiatric outpatients and their siblings. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 25(2), 192-200.
- Croft, C et al, (2007). Early adolescent outcomes of institutionally-deprived and nondeprived adoptees: II. Language as a protective factor and a vulnerable outcome. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48, 31–44.
- Dalen, M. (2001). School performances among internationally adopted children in Norway. Adoption Quarterly, 5(2), 39-57.
- Dalen, M. (1995). Learning difficulties among inter-country adopted children. Nordisk pedagogikk, 15 (No. 4), 195-208
- Davies, J., & Bledsoe, J. (2005). Prenatal alcohol and drug exposures in adoption. Pediatric Clinics of North America, 52, 1369–1393.
- Desmarais, C., Roeber, B. J., Smith, M. E., & Pollak, S. D. (2012). Sentence comprehension in post-institutionalized school-age children. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 55, 45-54
- Eigsti, I. M., Weitzman, C., Schuh, J. M., de Marchena, A., & Casey, B. J. (2011). Language and cognitive outcomes in internationally adopted children. Development and Psychopathology, 23, 629-646.
- Geren, J., Snedeker, J., & Ax, L. (2005). Starting over: a preliminary study of early lexical and syntactic development in internationally-adopted preschoolers. Seminars in Speech & Language, 26:44-54.
- Gindis (2008) Abrupt native language loss in international adoptees. Advance for Speech/Language Pathologists and Audiologists. 18(51): 5.
- Gindis, B. (2005). Cognitive, language, and educational issues of children adopted from overseas orphanages. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 4 (3): 290-315. Gindis, B. (1999) Language-related issues for international adoptees and adoptive families. In: T. Tepper, L. Hannon, D. Sandstrom, Eds. “International Adoption: Challenges and Opportunities.” PNPIC, Meadow Lands , PA. , pp. 98-108
- Glennen, S (2009) Speech and language guidelines for children adopted from abroad at older ages. Topics in language Disorders 29, 50-64.
- Glennen, S. (2007) Speech and language in children adopted internationally at older ages. Perspectives on Communication Disorders in Culturally and Linguistically Diverse Populations, 14, 17–20.
- Glennen, S., & Bright, B. J. (2005). Five years later: language in school-age internally adopted children. Seminars in Speech and Language, 26, 86-101.
- Glennen, S. & Masters, G. (2002). Typical and atypical language development in infants and toddlers adopted from Eastern Europe. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 44, 417-433
- Gordina, A (2009) Parent Handout: The Dream Referral, Unpublished Manuscript.
- Hough, S., & Kaczmarek, L. (2011). Language and reading outcomes in young children adopted from Eastern European orphanages. Journal of Early Intervention, 33, 51-57.
- Hwa-Froelich, D (2012) Childhood maltreatment and communication development. Perspectives on School-Based Issues, 13: 43-53;
- Jacobs, E., Miller, L. C., & Tirella, G. (2010). Developmental and behavioral performance of internationally adopted preschoolers: a pilot study. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 41, 15–29.
- Jenista, J., & Chapman, D. (1987). Medical problems of foreign-born adopted children. American Journal of Diseases of Children, 141, 298–302.
- Johnson, D. (2000). Long-term medical issues in international adoptees. Pediatric Annals, 29, 234–241.
- Judge, S. (2003). Developmental recovery and deficit in children adopted from Eastern European orphanages. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 34, 49–62.
- Krakow, R. A., & Roberts, J. (2003). Acquisitions of English vocabulary by young Chinese adoptees. Journal of Multilingual Communication Disorders, 1, 169-176
- Ladage, J. S. (2009). Medical issues in international adoption and their influence on language development. Topics in Language Disorders , 29 (1), 6-17.
- Loman, M. M., Wiik, K. L., Frenn, K. A., Pollak, S. D., & Gunnar, M. R. (2009). Post-institutionalized children’s development: growth, cognitive, and language outcomes. Journal of Developmental Behavioral Pediatrics, 30, 426–434.
- McLaughlin, B., Gesi Blanchard, A., & Osanai, Y. (1995). Assessing language development in bilingual preschool children. Washington, D.C.: National Clearinghouse for Bilingual Education.
- Miller, L., Chan, W., Litvinova, A., Rubin, A., Tirella, L., & Cermak, S. (2007). Medical diagnoses and growth of children residing in Russian orphanages. Acta Paediatrica, 96, 1765–1769.
- Miller, L., Chan, W., Litvinova, A., Rubin, A., Comfort, K., Tirella, L., et al. (2006). Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders in children residing in Russian orphanages: A phenotypic survey. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 30, 531–538.
- Miller, L. (2005). Preadoption counseling and evaluation of the referral. In L. Miller (Ed.), The Handbook of International Adoption Medicine (pp. 67-86). NewYork: Oxford.
- Pollock, K. E. (2005) Early language growth in children adopted from China: preliminary normative data. Seminars in Speech and Language, 26, 22-32.
- Roberts, J., Pollock, K., Krakow, R., Price, J., Fulmer, K., & Wang, P. (2005). Language development in preschool-aged children adopted from China. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 48, 93–107.
- Scott, K.A., Roberts, J.A., & Glennen, S. (2011). How well children who are internationally do adopted acquire language? A meta-analysis. Journal of Speech, Language and Hearing Research, 54. 1153-69.
- Scott, K.A., & Roberts, J. (2011). Making evidence-based decisions for children who are internationally adopted. Evidence-Based Practice Briefs. 6(3), 1-16.
- Scott, K.A., & Roberts, J. (2007) language development of internationally adopted children: the school-age years. Perspectives on Communication Disorders in Culturally and Linguistically Diverse Populations, 14: 12-17.
- Selman P. (2012a) Global trends in intercountry adoption 2000-2010. New York: National Council for Adoption.
- Selman P (2012b). The rise and fall of intercountry adoption in the 21st century. In: Gibbons, J.L., Rotabi, K.S, ed. Intercountry Adoption: Policies, Practices and Outcomes. London: Ashgate Press.
- Selman, P. (2010) “Intercountry adoption in Europe 1998–2009: patterns, trends and issues,” Adoption & Fostering, 34 (1): 4-19.
- Silliman, E. R., & Scott, C. M. (2009). Research-based oral language intervention routes to the academic language of literacy: Finding the right road. In S. A. Rosenfield & V. Wise Berninger (Eds.), Implementing evidence-based academic interventions in school (pp. 107–145). New York: Oxford University Press.
- Tarullo, A. R., Bruce, J., & Gunnar, M. (2007). False belief and emotion understanding in post-institutionalized children. Social Development, 16, 57-78
- Tarullo, A. & Gunnar, M. R. (2005). Institutional rearing and deficits in social relatedness: Possible mechanisms and processes. Cognitie, Creier, Comportament [Cognition, Brain, Behavior], 9, 329-342.
- Varavikova, E. A. & Balachova, T. N. (2010). Strategies to implement physician training in FAS prevention as a part of preventive care in primary health settings: P120.Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research. 34(8) Sup 3:119A.
- Welsh, J. A., & Viana, A. G. (2012). Developmental outcomes of children adopted internationally. Adoption Quarterly, 15, 241-264.
APD Update: New Developments on an Old Controversy
 In the past two years, I wrote a series of research-based posts (HERE and HERE) regarding the validity of (Central) Auditory Processing Disorder (C/APD) as a standalone diagnosis as well as questioned the utility of it for classification purposes in the school setting.
In the past two years, I wrote a series of research-based posts (HERE and HERE) regarding the validity of (Central) Auditory Processing Disorder (C/APD) as a standalone diagnosis as well as questioned the utility of it for classification purposes in the school setting.
Once again I want to reiterate that I was in no way disputing the legitimate symptoms (e.g., difficulty processing language, difficulty organizing narratives, difficulty decoding text, etc.), which the students diagnosed with “CAPD” were presenting with.
Rather, I was citing research to indicate that these symptoms were indicative of broader linguistic-based deficits, which required targeted linguistic/literacy-based interventions rather than recommendations for specific prescriptive programs (e.g., CAPDOTS, Fast ForWord, etc.), or mere accommodations.
I was also significantly concerned that overfocus on the diagnosis of (C)APD tended to obscure REAL, language-based deficits in children and forced SLPs to address erroneous therapeutic targets based on AuD recommendations or restricted them to a receipt of mere accommodations rather than rightful therapeutic remediation. Continue reading APD Update: New Developments on an Old Controversy







