 Today, I’d like to talk about speech and language assessments of children under three years of age. Namely, the quality of these assessments. Let me be frank, I am not happy with what I am seeing. Often times, when I receive a speech-language report on a child under three years of age, I am struck by how little functional information it contains about the child’s linguistic strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, conversations with parents often reveal that at best the examiner spent no more than half an hour or so playing with the child and performed very limited functional testing of their actual abilities. Instead, they interviewed the parent and based their report on parental feedback alone. Consequently, parents often end up with a report of very limited value, which does not contain any helpful information on how delayed is the child as compared to peers their age.
Today, I’d like to talk about speech and language assessments of children under three years of age. Namely, the quality of these assessments. Let me be frank, I am not happy with what I am seeing. Often times, when I receive a speech-language report on a child under three years of age, I am struck by how little functional information it contains about the child’s linguistic strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, conversations with parents often reveal that at best the examiner spent no more than half an hour or so playing with the child and performed very limited functional testing of their actual abilities. Instead, they interviewed the parent and based their report on parental feedback alone. Consequently, parents often end up with a report of very limited value, which does not contain any helpful information on how delayed is the child as compared to peers their age.
So today I like to talk about what information should such speech-language reports should contain. For the purpose of this particular post, I will choose a particular developmental age at which children at risk of language delay are often assessed by speech-language pathologists. Below you will find what information I typically like to include in these reports as well as developmental milestones for children 30 months or 2.5 years of age.
 Why 30 months, you may ask? Well, there isn’t really any hard science to it. It’s just that I noticed that a significant percentage of parents who were already worried about their children’s speech-language abilities when they were younger, begin to act upon those worries as the child is nearing 3 years of age and their abilities are not improving or are not commensurate with other peers their age.
Why 30 months, you may ask? Well, there isn’t really any hard science to it. It’s just that I noticed that a significant percentage of parents who were already worried about their children’s speech-language abilities when they were younger, begin to act upon those worries as the child is nearing 3 years of age and their abilities are not improving or are not commensurate with other peers their age.
So here is the information I include in such reports (after I’ve gathered pertinent background information in the form of relevant intakes and questionnaires, of course). Naturally, detailed BACKGROUND HISTORY section is a must! Prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal development should be prominently featured there. All pertinent medical history needs to get documented as well as all of the child’s developmental milestones in the areas of cognition, emotional development, fine and gross motor function, and of course speech and language. Here, I also include a family history of red flags: international or domestic adoption of the child (if relevant) as well as familial speech and language difficulties, intellectual impairment, psychiatric disorders, special education placements, or documented deficits in the areas of literacy (e.g., reading, writing, and spelling). After all, if any of the above issues are present in isolation or in combination, the risk for language and literacy deficits increases exponentially, and services are strongly merited for the child in question.
For bilingual children, the next section will cover LANGUAGE BACKGROUND AND USE. Here, I describe how many and which languages are spoken in the home and how well does the child understand and speak any or all of these languages (as per parental report based on questionnaires).
After that, I move on to describe the child’s ADAPTIVE BEHAVIOR during the assessment. In this section, I cover emotional relatedness, joint attention, social referencing, attention skills, communicative frequency, communicative intent, communicative functions, as well as any and all unusual behaviors noted during the therapy session (e.g., refusal, tantrums, perseverations, echolalia, etc.) Then I move on to PLAY SKILLS. For the purpose of play assessment, I use the Revised Westby Play Scale (Westby, 2000). In this section, I describe where the child is presently with respect to play skills, and where they actually need to be developmentally (excerpt below).
“During today’s assessment, LS’s play skills were judged to be significantly reduced for his age. A child of LS’s age (30 months) is expected to engage in a number of isolated pretend play activities with realistic props to represent daily experiences (playing house) as well as less frequently experienced events (e.g., reenacting a doctor’s visit, etc.) (corresponds to Stage VI on the Westby Play Scale, Revised Westby Play Scale (Westby, 2000)). Contrastingly, LS presented with limited repertoire routines, which were characterized primarily by exploration of toys, such as operating simple cause and effect toys (given modeling) or taking out and then putting back in playhouse toys. LS’s parents confirmed that the above play schemas were representative of play interactions at home as well. Today’s LS’s play skills were judged to be approximately at Stage II (13 – 17 months) on the Westby Play Scale, (Revised Westby Play Scale (Westby, 2000)) which is significantly reduced for a child of LS’s age, since it is almost approximately ±15 months behind his peers. Thus, based on today’s play assessment, LS’s play skills require therapeutic intervention. “
Sections on AUDITORY FUNCTION, PERIPHERAL ORAL MOTOR EXAM, VOCAL PARAMETERS, FLUENCY AND RESONANCE (and if pertinent FEEDING and SWALLOWING follow) (more on that in another post).
Now, it’s finally time to get to the ‘meat and potatoes’ of the report ARTICULATION AND PHONOLOGY as well as RECEPTIVE and EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE (more on PRAGMATIC ASSESSMENT in another post).
First, here’s what I include in the ARTICULATION AND PHONOLOGY section of the report.
- Phonetic inventory: all the sounds the child is currently producing including (short excerpt below):
- Consonants: plosive (/p/, /b/, /m/), alveolar (/t/, /d/), velar (/k/, /g/), glide (/w/), nasal (/n/, /m/) glottal (/h/)
- Vowels and diphthongs: ( /a/, /e/, /i/, /o/, /u/, /ou/, /ai/)
- Phonotactic repertoire: What type of words comprised of how many syllables and which consonant-vowel variations the child is producing (excerpt below)
- LS primarily produced one syllable words consisting of CV (e.g., ke, di), CVC (e.g., boom), VCV (e.g., apo) syllable shapes, which is reduced for a child his age.
- Speech intelligibility in known and unknown contexts
- Phonological processes analysis
Now that I have described what the child is capable of speech-wise, I discuss where the child needs to be developmentally:
“A child of LS’s age (30 months) is expected to produce additional consonants in initial word position (k, l, s, h), some consonants (t, d, m, n, s, z) in final word position (Watson & Scukanec, 1997b), several consonant clusters (pw, bw, -nd, -ts) (Stoel-Gammon, 1987) as well as evidence a more sophisticated syllable shape structure (e.g., CVCVC) Furthermore, a 30 month old child is expected to begin monitoring and repairing own utterances, adjusting speech to different listeners, as well as practicing sounds, words, and early sentences (Clark, adapted by Owens, 1996, p. 386) all of which LS is not performing at this time. Based on above developmental norms, LS’s phonological abilities are judged to be significantly below age-expectancy at this time. Therapy is recommended in order to improve LS’s phonological skills.”
 At this point, I am ready to move on to the language portion of the assessment. Here it is important to note that a number of assessments for toddlers under 3 years of age contain numerous limitations. Some such as REEL-3 or Rosetti (a criterion-referenced vs. normed-referenced instrument) are observational or limitedly interactive in nature, while others such as PLS-5, have a tendency to over inflate scores, resulting in a significant number of children not qualifying for rightfully deserved speech-language therapy services. This is exactly why it’s so important that SLPs have a firm knowledge of developmental milestones! After all, after they finish describing what the child is capable of, they then need to describe what the developmental expectations are for a child this age (excerpts below).
At this point, I am ready to move on to the language portion of the assessment. Here it is important to note that a number of assessments for toddlers under 3 years of age contain numerous limitations. Some such as REEL-3 or Rosetti (a criterion-referenced vs. normed-referenced instrument) are observational or limitedly interactive in nature, while others such as PLS-5, have a tendency to over inflate scores, resulting in a significant number of children not qualifying for rightfully deserved speech-language therapy services. This is exactly why it’s so important that SLPs have a firm knowledge of developmental milestones! After all, after they finish describing what the child is capable of, they then need to describe what the developmental expectations are for a child this age (excerpts below).
RECEPTIVE LANGUAGE
“LS’s receptive language abilities were judged to be scattered between 11-17 months of age (as per clinical observations as well as informal PLS-5 and REEL-3 findings), which is also consistent with his play skills abilities (see above). During the assessment LS was able to appropriately understand prohibitive verbalizations (e.g., “No”, “Stop”), follow simple 1 part directions (when repeated and combined with gestures), selectively attend to speaker when his name was spoken (behavioral), perform a routine activity upon request (when combined with gestures), retrieve familiar objects from nearby (when provided with gestures), identify several major body parts (with prompting) on a doll only, select a familiar object when named given repeated prompting, point to pictures of familiar objects in books when named by adult, as well as respond to yes/no questions by using head shakes and head nods. This is significantly below age-expectancy.
A typically developing child 30 months of age is expected to spontaneously follow (without gestures, cues or prompts) 2+ step directives, follow select commands that require getting objects out of sight, answer simple “wh” questions (what, where, who), understand select spatial concepts, (in, off, out of, etc), understand select pronouns (e.g., me, my, your), identify action words in pictures, understand concept sizes (‘big’, ‘little’), identify simple objects according to their function, identify select clothing items such as shoes, shirt, pants, hat (on self or caregiver) as well as understand names of farm animals, everyday foods, and toys. Therapeutic intervention is recommended in order to increase LS’s receptive language abilities.
EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE:
“During today’s assessment, LS’s expressive language skills were judged to be scattered between 10-15 months of age (as per clinical observations as well as informal PLS-5 and REEL-3 findings). LS was observed to communicate primarily via proto-imperative gestures (requesting and object via eye gaze, reaching) as well as proto-declarative gestures (showing an object via eye gaze, reaching, and pointing). Additionally, LS communicated via vocalizations, head nods, and head shakes. According to parental report, at this time LS’s speaking vocabulary consists of approximately 15-20 words (see word lists below). During the assessment LS was observed to spontaneously produce a number of these words when looking at a picture book, playing with toys, and participating in action based play activities with Mrs. S and clinician. LS was also observed to produce a number of animal sounds when looking at select picture books and puzzles. For therapy planning purposes, it is important to note that LS was observed to imitate more sounds and words, when they were supported by action based play activities (when words and sounds were accompanied by a movement initiated by clinician and then imitated by LS). Today LS was observed to primarily communicate via a very limited number of imitated and spontaneous one word utterances that labeled basic objects and pictures in his environment, which is significantly reduced for his age.
A typically developing child of LS’s chronological age (30 months) is expected to possess a minimum vocabulary of 200+ words (Rescorla, 1989), produce 2-4 word utterance combinations (e.g., noun + verb, verb + noun + location, verb + noun + adjective, etc), in addition to asking 2-3 word questions as well as maintaining a topic for 2+ conversational turns. Therapeutic intervention is recommended in order to increase LS’s expressive language abilities.”
Here you have a few speech-language evaluation excerpts which describe not just what the child is capable of but where the child needs to be developmentally. Now it’s just a matter of summarizing my IMPRESSIONS (child’s strengths and needs), RECOMMENDATIONS as well as SUGGESTED (long and short term) THERAPY GOALS. Now the parents have some understanding regarding their child’s strengths and needs. From here, they can also track their child’s progress in therapy as they now have some idea to what it can be compared to.
 Now I know that many of you will tell me, that this is a ‘perfect world’ evaluation conducted by a private therapist with an unlimited amount of time on her hands. And to some extent, many of you will be right! Yes, such an evaluation was a result of more than 30 minutes spent face-to-face with the child. All in all, it took probably closer to 90 minutes of face to face time to complete it and a few hours to write. And yes, this is a luxury only a few possess and many therapists in the early intervention system lack. But in the long run, such evaluations pay dividends not only, obviously, to your clients but to SLPs who perform them. They enhance and grow your reputation as an evaluating therapist. They even make sense from a business perspective. If you are well-known and highly sought after due to your evaluating expertise, you can expect to be compensated for your time, accordingly. This means that if you decide that your time and expertise are worth private pay only (due to poor insurance reimbursement or low EI rates), you can be sure that parents will learn to appreciate your thoroughness and will choose you over other providers.
Now I know that many of you will tell me, that this is a ‘perfect world’ evaluation conducted by a private therapist with an unlimited amount of time on her hands. And to some extent, many of you will be right! Yes, such an evaluation was a result of more than 30 minutes spent face-to-face with the child. All in all, it took probably closer to 90 minutes of face to face time to complete it and a few hours to write. And yes, this is a luxury only a few possess and many therapists in the early intervention system lack. But in the long run, such evaluations pay dividends not only, obviously, to your clients but to SLPs who perform them. They enhance and grow your reputation as an evaluating therapist. They even make sense from a business perspective. If you are well-known and highly sought after due to your evaluating expertise, you can expect to be compensated for your time, accordingly. This means that if you decide that your time and expertise are worth private pay only (due to poor insurance reimbursement or low EI rates), you can be sure that parents will learn to appreciate your thoroughness and will choose you over other providers.
So, how about it? Can you give it a try? Trust me, it’s worth it!
Selected References:
- Owens, R. E. (1996). Language development: An introduction (4th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
- Rescorla, L. (1989). The Language Development Survey: A screening tool for delayed language in toddlers. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 54, 587–599.
- Selby, J. C., Robb, M. P., & Gilbert, H. R. (2000). Normal vowel articulations between 15 and 36 months of age. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics, 14, 255-266.
- Stoel-Gammon, C. (1987). Phonological skills of 2-year-olds. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 18, 323-329.
- Watson, M. M., & Scukanec, G. P. (1997b). Profiling the phonological abilities of 2-year-olds: A longitudinal investigation. Child Language Teaching and Therapy, 13, 3-14.
For more information on EI Assessments click on any of the below posts:

 For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the
For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the  Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the
Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the 
 Today, I’d like to talk about speech and language assessments of children under three years of age. Namely, the quality of these assessments. Let me be frank, I am not happy with what I am seeing. Often times, when I receive a speech-language report on a child under three years of age, I am struck by how little functional information it contains about the child’s linguistic strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, conversations with parents often reveal that at best the examiner spent no more than half an hour or so playing with the child and performed very limited functional testing of their actual abilities. Instead, they interviewed the parent and based their report on parental feedback alone. Consequently, parents often end up with a report of very limited value, which does not contain any helpful information on how delayed is the child as compared to peers their age.
Today, I’d like to talk about speech and language assessments of children under three years of age. Namely, the quality of these assessments. Let me be frank, I am not happy with what I am seeing. Often times, when I receive a speech-language report on a child under three years of age, I am struck by how little functional information it contains about the child’s linguistic strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, conversations with parents often reveal that at best the examiner spent no more than half an hour or so playing with the child and performed very limited functional testing of their actual abilities. Instead, they interviewed the parent and based their report on parental feedback alone. Consequently, parents often end up with a report of very limited value, which does not contain any helpful information on how delayed is the child as compared to peers their age. Why 30 months, you may ask? Well, there isn’t really any hard science to it. It’s just that I noticed that a significant percentage of parents who were already worried about their children’s speech-language abilities when they were younger, begin to act upon those worries as the child is nearing 3 years of age and their abilities are not improving or are not commensurate with other peers their age.
Why 30 months, you may ask? Well, there isn’t really any hard science to it. It’s just that I noticed that a significant percentage of parents who were already worried about their children’s speech-language abilities when they were younger, begin to act upon those worries as the child is nearing 3 years of age and their abilities are not improving or are not commensurate with other peers their age. At this point, I am ready to move on to the language portion of the assessment. Here it is important to note that a number of assessments for toddlers under 3 years of age contain numerous limitations. Some such as REEL-3 or Rosetti (a criterion-referenced vs. normed-referenced instrument) are observational or limitedly interactive in nature, while others such as PLS-5, have a tendency to
At this point, I am ready to move on to the language portion of the assessment. Here it is important to note that a number of assessments for toddlers under 3 years of age contain numerous limitations. Some such as REEL-3 or Rosetti (a criterion-referenced vs. normed-referenced instrument) are observational or limitedly interactive in nature, while others such as PLS-5, have a tendency to  Now I know that many of you will tell me, that this is a ‘perfect world’ evaluation conducted by a private therapist with an unlimited amount of time on her hands. And to some extent, many of you will be right! Yes, such an evaluation was a result of more than 30 minutes spent face-to-face with the child. All in all, it took probably closer to 90 minutes of face to face time to complete it and a few hours to write. And yes, this is a luxury only a few possess and many therapists in the early intervention system lack. But in the long run, such evaluations pay dividends not only, obviously, to your clients but to SLPs who perform them. They enhance and grow your reputation as an evaluating therapist. They even make sense from a business perspective. If you are well-known and highly sought after due to your evaluating expertise, you can expect to be compensated for your time, accordingly. This means that if you decide that your time and expertise are worth private pay only (due to poor insurance reimbursement or low EI rates), you can be sure that parents will learn to appreciate your thoroughness and will choose you over other providers.
Now I know that many of you will tell me, that this is a ‘perfect world’ evaluation conducted by a private therapist with an unlimited amount of time on her hands. And to some extent, many of you will be right! Yes, such an evaluation was a result of more than 30 minutes spent face-to-face with the child. All in all, it took probably closer to 90 minutes of face to face time to complete it and a few hours to write. And yes, this is a luxury only a few possess and many therapists in the early intervention system lack. But in the long run, such evaluations pay dividends not only, obviously, to your clients but to SLPs who perform them. They enhance and grow your reputation as an evaluating therapist. They even make sense from a business perspective. If you are well-known and highly sought after due to your evaluating expertise, you can expect to be compensated for your time, accordingly. This means that if you decide that your time and expertise are worth private pay only (due to poor insurance reimbursement or low EI rates), you can be sure that parents will learn to appreciate your thoroughness and will choose you over other providers. For bilingual and monolingual SLPs working with bilingual and multicultural children, the question of: “Is it a difference or a disorder?” arises on a daily basis as they attempt to navigate the myriad of difficulties they encounter in their attempts at appropriate diagnosis of speech, language, and literacy disorders.
For bilingual and monolingual SLPs working with bilingual and multicultural children, the question of: “Is it a difference or a disorder?” arises on a daily basis as they attempt to navigate the myriad of difficulties they encounter in their attempts at appropriate diagnosis of speech, language, and literacy disorders. For that purpose, I’ve recently created a
For that purpose, I’ve recently created a 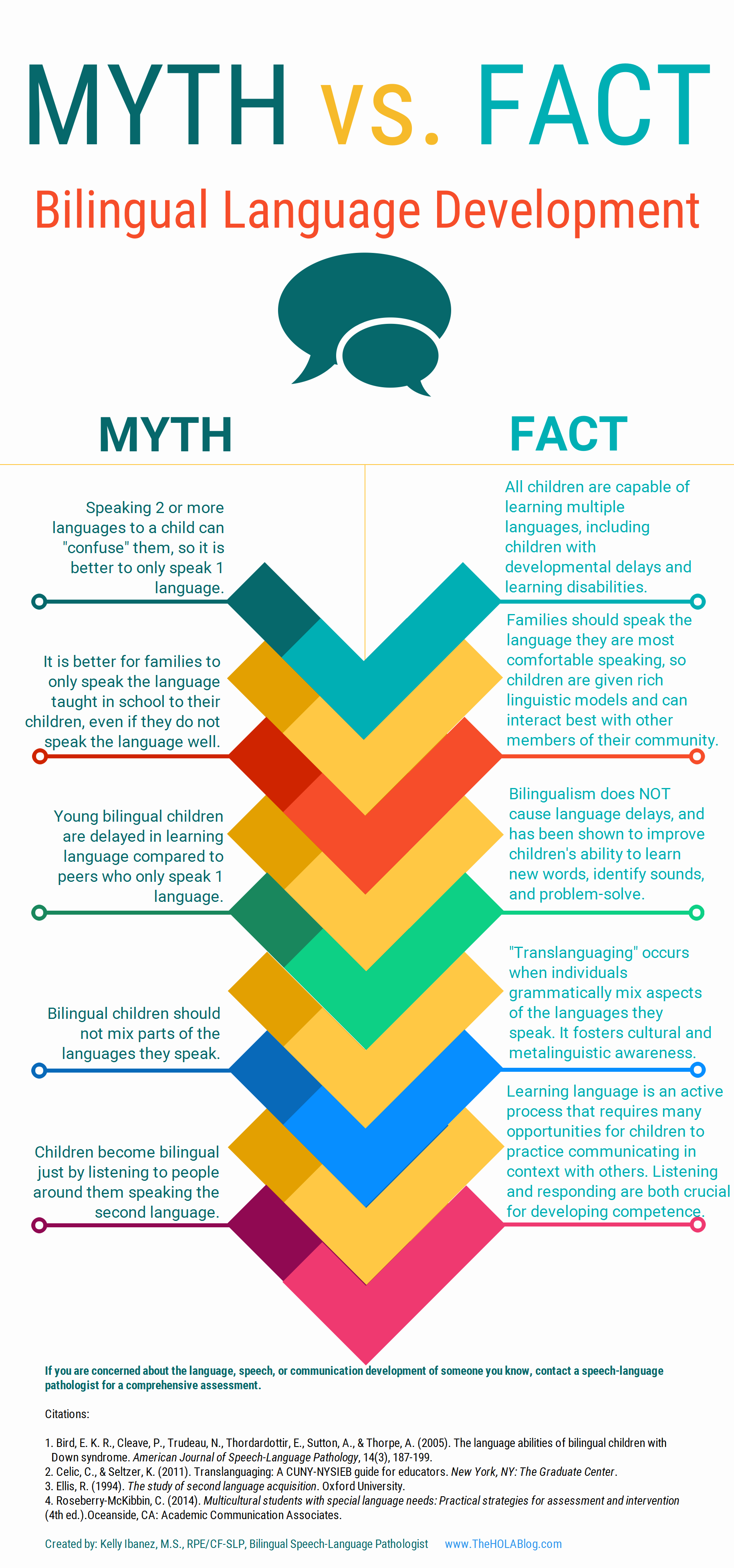 Let’s start with an excellent free infographic entitled from the Hola Blog “
Let’s start with an excellent free infographic entitled from the Hola Blog “ Next up, is a great archive which contains
Next up, is a great archive which contains  For SLPs working with Russian-speaking children the following links pertinent to assessment, intervention and language transference may be helpful:
For SLPs working with Russian-speaking children the following links pertinent to assessment, intervention and language transference may be helpful:
 When many of us think of such labels as “language disorder” or “learning disability”, very infrequently do adolescents (students 13-18 years of age) come to mind. Even today, much of the research in the field of pediatric speech pathology involves preschool and school-aged children under 12 years of age.
When many of us think of such labels as “language disorder” or “learning disability”, very infrequently do adolescents (students 13-18 years of age) come to mind. Even today, much of the research in the field of pediatric speech pathology involves preschool and school-aged children under 12 years of age.


 As a speech language pathologist (SLP) who works in an outpatient psychiatric school-based setting, I frequently review incoming students previous speech language evaluation reports. There are a number of trends I see in these reports which I have written about in the past as well as planned on writing about in the future.
As a speech language pathologist (SLP) who works in an outpatient psychiatric school-based setting, I frequently review incoming students previous speech language evaluation reports. There are a number of trends I see in these reports which I have written about in the past as well as planned on writing about in the future.


 Recently, I’ve published an article in
Recently, I’ve published an article in  Graduation time is rapidly approaching and many graduate speech language pathology students are getting ready to begin their first days in the workforce. When it comes to juggling caseloads and managing schedules, time is money and efficiency is the key to success. Consequently, a few years ago I created SLP Efficiency Bundles™, which are materials highly useful for Graduate SLPs working with pediatric clients. These materials are organized by areas of focus for efficient and effective screening, assessment, and treatment of speech and language disorders.
Graduation time is rapidly approaching and many graduate speech language pathology students are getting ready to begin their first days in the workforce. When it comes to juggling caseloads and managing schedules, time is money and efficiency is the key to success. Consequently, a few years ago I created SLP Efficiency Bundles™, which are materials highly useful for Graduate SLPs working with pediatric clients. These materials are organized by areas of focus for efficient and effective screening, assessment, and treatment of speech and language disorders.