 Those of you who have previously read my blog know that I rarely use children’s games to address language goals. However, over the summer I have been working on improving executive function abilities (EFs) of some of the language impaired students on my caseload. As such, I found select children’s games to be highly beneficial for improving language-based executive function abilities.
Those of you who have previously read my blog know that I rarely use children’s games to address language goals. However, over the summer I have been working on improving executive function abilities (EFs) of some of the language impaired students on my caseload. As such, I found select children’s games to be highly beneficial for improving language-based executive function abilities.
For those of you who are only vaguely familiar with this concept, executive functions are higher level cognitive processes involved in the inhibition of thought, action, and emotion, which located in the prefrontal cortex of the frontal lobe of the brain. The development of executive functions begins in early infancy; but it can be easily disrupted by a number of adverse environmental and organic experiences (e.g., psychosocial deprivation, trauma). Furthermore, research in this area indicates that the children with language impairments present with executive function weaknesses which require remediation.
EF components include working memory, inhibitory control, planning, and set-shifting.
- Working memory
- Ability to store and manipulate information in mind over brief periods of time
- Inhibitory control
- Suppressing responses that are not relevant to the task
- Set-shifting
- Ability to shift behavior in response to changes in tasks or environment
Simply put, EFs contribute to the child’s ability to sustain attention, ignore distractions, and succeed in academic settings. By now some of you must be wondering: “So what does Hedbanz have to do with any of it?”
Well, Hedbanz is a quick-paced multiplayer (2-6 people) game of “What Am I?” for children ages 7 and up. Players get 3 chips and wear a “picture card” in their headband. They need to ask questions in rapid succession to figure out what they are. “Am I fruit?” “Am I a dessert?” “Am I sports equipment?” When they figure it out, they get rid of a chip. The first player to get rid of all three chips wins.
The game sounds deceptively simple. Yet if any SLPs or parents have ever played that game with their language impaired students/children as they would be quick to note how extraordinarily difficult it is for the children to figure out what their card is. Interestingly, in my clinical experience, I’ve noticed that it’s not just moderately language impaired children who present with difficulty playing this game. Even my bright, average intelligence teens, who have passed vocabulary and semantic flexibility testing (such as the WORD Test 2-Adolescent or the Vocabulary Awareness subtest of the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy ) significantly struggle with their language organization when playing this game.
So what makes Hedbanz so challenging for language impaired students? Primarily, it’s the involvement and coordination of the multiple executive functions during the game. In order to play Hedbanz effectively and effortlessly, the following EF involvement is needed:
- Task Initiation
- Students with executive function impairments will often “freeze up” and as a result may have difficulty initiating the asking of questions in the game because many will not know what kind of questions to ask, even after extensive explanations and elaborations by the therapist.
- Organization
- Students with executive function impairments will present with difficulty organizing their questions by meaningful categories and as a result will frequently lose their track of thought in the game.
- Working Memory
- This executive function requires the student to keep key information in mind as well as keep track of whatever questions they have already asked.
- Flexible Thinking
- This executive function requires the student to consider a situation from multiple angles in order to figure out the quickest and most effective way of arriving at a solution. During the game, students may present with difficulty flexibly generating enough organizational categories in order to be effective participants.
- Impulse Control
- Many students with difficulties in this area may blurt out an inappropriate category or in an appropriate question without thinking it through first.
- They may also present with difficulty set-shifting. To illustrate, one of my 13-year-old students with ASD, kept repeating the same question when it was his turn, despite the fact that he was informed by myself as well as other players of the answer previously.
- Emotional Control
- This executive function will help students with keeping their emotions in check when the game becomes too frustrating. Many students of difficulties in this area will begin reacting behaviorally when things don’t go their way and they are unable to figure out what their card is quickly enough. As a result, they may have difficulty mentally regrouping and reorganizing their questions when something goes wrong in the game.
- Self-Monitoring
- This executive function allows the students to figure out how well or how poorly they are doing in the game. Students with poor insight into own abilities may present with difficulty understanding that they are doing poorly and may require explicit instruction in order to change their question types.
- Planning and Prioritizing
- Students with poor abilities in this area will present with difficulty prioritizing their questions during the game.
Consequently, all of the above executive functions can be addressed via language-based goals. However, before I cover that, I’d like to review some of my session procedures first.
Typically, long before game initiation, I use the cards from the game to prep the students by teaching them how to categorize and classify presented information so they effectively and efficiently play the game.
 Rather than using the “tip cards”, I explain to the students how to categorize information effectively.
Rather than using the “tip cards”, I explain to the students how to categorize information effectively.
This, in turn, becomes a great opportunity for teaching students relevant vocabulary words, which can be extended far beyond playing the game.
I begin the session by explaining to the students that pretty much everything can be roughly divided into two categories animate (living) or inanimate (nonliving) things. I explain that humans, animals, as well as plants belong to the category of living things, while everything else belongs to the category of inanimate objects. I further divide the category of inanimate things into naturally existing and man-made items. I explain to the students that the naturally existing category includes bodies of water, landmarks, as well as things in space (moon, stars, sky, sun, etc.). In contrast, things constructed in factories or made by people would be example of man-made objects (e.g., building, aircraft, etc.)
When I’m confident that the students understand my general explanations, we move on to discuss further refinement of these broad categories. If a student determines that their card belongs to the category of living things, we discuss how from there the student can further determine whether they are an animal, a plant, or a human. If a student determined that their card belongs to the animal category, we discuss how we can narrow down the options of figuring out what animal is depicted on their card by asking questions regarding their habitat (“Am I a jungle animal?”), and classification (“Am I a reptile?”). From there, discussion of attributes prominently comes into play. We discuss shapes, sizes, colors, accessories, etc., until the student is able to confidently figure out which animal is depicted on their card.
In contrast, if the student’s card belongs to the inanimate category of man-made objects, we further subcategorize the information by the object’s location (“Am I found outside or inside?”; “Am I found in ___ room of the house?”, etc.), utility (“Can I be used for ___?”), as well as attributes (e.g., size, shape, color, etc.)
Thus, in addition to improving the students’ semantic flexibility skills (production of definitions, synonyms, attributes, etc.) the game teaches the students to organize and compartmentalize information in order to effectively and efficiently arrive at a conclusion in the most time expedient fashion.

Now, we are ready to discuss what type of EF language-based goals, SLPs can target by simply playing this game.
1. Initiation: Student will initiate questioning during an activity in __ number of instances per 30-minute session given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
2. Planning: Given a specific routine, student will verbally state the order of steps needed to complete it with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
3. Working Memory: Student will repeat clinician provided verbal instructions pertaining to the presented activity, prior to its initiation, with 80% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
4. Flexible Thinking: Following a training by the clinician, student will generate at least __ questions needed for task completion (e.g., winning the game) with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
5. Organization: Student will use predetermined written/visual cues during an activity to assist self with organization of information (e.g., questions to ask) with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
6. Impulse Control: During the presented activity the student will curb blurting out inappropriate responses (by silently counting to 3 prior to providing his response) in __ number of instances per 30 minute session given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
7. Emotional Control: When upset, student will verbalize his/her frustration (vs. behavioral activing out) in __ number of instances per 30 minute session given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
8. Self-Monitoring: Following the completion of an activity (e.g., game) student will provide insight into own strengths and weaknesses during the activity (recap) by verbally naming the instances in which s/he did well, and instances in which s/he struggled with __% accuracy given (maximal, moderate, minimal) type of ___ (phonemic, semantic, etc.) prompts and __ (visual, gestural, tactile, etc.) cues by the clinician.
There you have it. This one simple game doesn’t just target a plethora of typical expressive language goals. It can effectively target and improve language-based executive function goals as well. Considering the fact that it sells for approximately $12 on Amazon.com, that’s a pretty useful therapy material to have in one’s clinical tool repertoire. For fancier versions, clinicians can use “Jeepers Peepers” photo card sets sold by Super Duper Inc. Strapped for cash, due to highly limited budget? You can find plenty of free materials online if you simply input “Hedbanz cards” in your search query on Google. So have a little fun in therapy, while your students learn something valuable in the process and play Hedbanz today!
Related Smart Speech Therapy Resources:
 Today’s guest post on genetic syndromes comes from Rebecca Freeh Thornburg, who is contributing on CHARGE Syndrome.
Today’s guest post on genetic syndromes comes from Rebecca Freeh Thornburg, who is contributing on CHARGE Syndrome. Here’s a familiar scenario to many SLPs. You’ve administered several standardized language tests to your student (e.g., CELF-5 & TILLS). You expected to see roughly similar scores across tests. Much to your surprise, you find that while your student attained somewhat average scores on one assessment, s/he had completely bombed the second assessment, and you have no idea why that happened.
Here’s a familiar scenario to many SLPs. You’ve administered several standardized language tests to your student (e.g., CELF-5 & TILLS). You expected to see roughly similar scores across tests. Much to your surprise, you find that while your student attained somewhat average scores on one assessment, s/he had completely bombed the second assessment, and you have no idea why that happened. Actually, my last statement is rather debatable. A careful perusal of the CELF – 5 reveals that its normative sample of 3000 children included a whopping 23% of children with language-related disabilities. In fact, the folks from the
Actually, my last statement is rather debatable. A careful perusal of the CELF – 5 reveals that its normative sample of 3000 children included a whopping 23% of children with language-related disabilities. In fact, the folks from the 
 The TILLS is a far less known assessment than the CELF-5 yet in the few years it has been out on the market it really made its presence felt by being a solid assessment tool due to its valid and reliable psychometric properties. Again, the venerable Dr. Carol Westby had already done such an excellent job reviewing its
The TILLS is a far less known assessment than the CELF-5 yet in the few years it has been out on the market it really made its presence felt by being a solid assessment tool due to its valid and reliable psychometric properties. Again, the venerable Dr. Carol Westby had already done such an excellent job reviewing its  Then there’s a variation of this assertion, which I have seen in several Facebook groups: “
Then there’s a variation of this assertion, which I have seen in several Facebook groups: “



 High comorbidity between language and psychiatric disorders has been well documented (Beitchman, Cohen, Konstantaras, & Tannock, 1996; Cohen, Barwick, Horodezky, Vallence, & Im, 1998; Toppelberg & Shapiro, 2000). However, a lesser known fact is that there’s also a significant under-diagnosis of language impairments in children with psychiatric disorders.
High comorbidity between language and psychiatric disorders has been well documented (Beitchman, Cohen, Konstantaras, & Tannock, 1996; Cohen, Barwick, Horodezky, Vallence, & Im, 1998; Toppelberg & Shapiro, 2000). However, a lesser known fact is that there’s also a significant under-diagnosis of language impairments in children with psychiatric disorders.  Two years ago I wrote a blog post entitled: “
Two years ago I wrote a blog post entitled: “
 First up is the concept of learning vs. generalization. Here Dr. Kamhi discusses that some clinicians still possess an “outdated behavioral view of learning” in our field, which is not theoretically and clinically useful. He explains that when we are talking about generalization – what children truly have a difficulty with is “transferring narrow limited rules to new situations“. “Children with language and learning problems will have difficulty acquiring broad-based rules and modifying these rules once acquired, and they also will be more vulnerable to performance demands on speech production and comprehension (Kamhi, 1988)” (93). After all, it is not “reasonable to expect children to use language targets consistently after a brief period of intervention” and while we hope that “language intervention [is] designed to lead children with language disorders to acquire broad-based language rules” it is a hugely difficult task to undertake and execute.
First up is the concept of learning vs. generalization. Here Dr. Kamhi discusses that some clinicians still possess an “outdated behavioral view of learning” in our field, which is not theoretically and clinically useful. He explains that when we are talking about generalization – what children truly have a difficulty with is “transferring narrow limited rules to new situations“. “Children with language and learning problems will have difficulty acquiring broad-based rules and modifying these rules once acquired, and they also will be more vulnerable to performance demands on speech production and comprehension (Kamhi, 1988)” (93). After all, it is not “reasonable to expect children to use language targets consistently after a brief period of intervention” and while we hope that “language intervention [is] designed to lead children with language disorders to acquire broad-based language rules” it is a hugely difficult task to undertake and execute.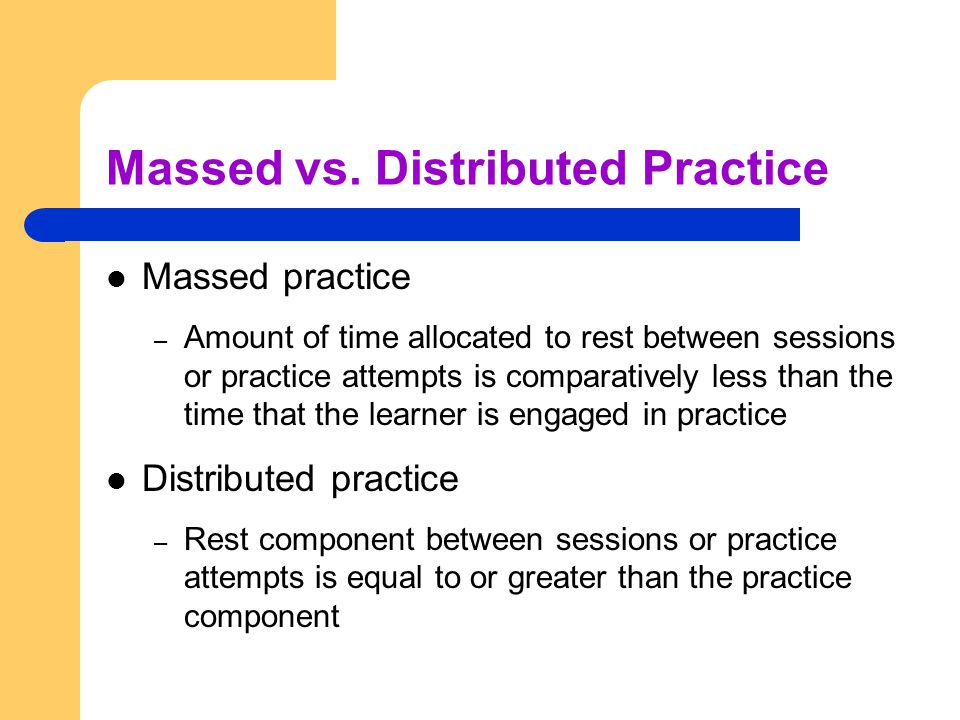 After that, Dr. Kamhi addresses the concept of distributed practice (spacing of intervention) and how important it is for teaching children with language disorders. He points out that a number of recent studies have found that “spacing and distribution of teaching episodes have more of an impact on treatment outcomes than
After that, Dr. Kamhi addresses the concept of distributed practice (spacing of intervention) and how important it is for teaching children with language disorders. He points out that a number of recent studies have found that “spacing and distribution of teaching episodes have more of an impact on treatment outcomes than 
 From there lets us take a look at Dr. Kamhi’s recommendations for grammar and syntax. Grammatical development goes much further than addressing Brown’s morphemes in therapy and calling it a day. As such, it is important to understand that children with developmental language disorders (DLD) (#DevLang) do not have difficulty acquiring all morphemes. Rather studies have shown that they have difficulty learning grammatical morphemes that reflect tense and agreement (e.g., third-person singular, past tense, auxiliaries, copulas, etc.). As such, use of measures developed by
From there lets us take a look at Dr. Kamhi’s recommendations for grammar and syntax. Grammatical development goes much further than addressing Brown’s morphemes in therapy and calling it a day. As such, it is important to understand that children with developmental language disorders (DLD) (#DevLang) do not have difficulty acquiring all morphemes. Rather studies have shown that they have difficulty learning grammatical morphemes that reflect tense and agreement (e.g., third-person singular, past tense, auxiliaries, copulas, etc.). As such, use of measures developed by  Dr. Kamhi supports the above point by providing an example of two passages. One, which describes a random order of events, and another which follows a logical order of events. He then points out that the randomly ordered story relies exclusively on attention and memory in terms of “sequencing”, while the second story reduces demands on memory due to its logical flow of events. As such, he points out that retelling deficits seemingly related to sequencing, tend to be actually due to “limitations in attention, working memory, and/or conceptual knowledge“. Hence, instead of targeting sequencing abilities in therapy, SLPs should instead use contextualized language intervention to target aspects of narrative development (macro and microstructural elements).
Dr. Kamhi supports the above point by providing an example of two passages. One, which describes a random order of events, and another which follows a logical order of events. He then points out that the randomly ordered story relies exclusively on attention and memory in terms of “sequencing”, while the second story reduces demands on memory due to its logical flow of events. As such, he points out that retelling deficits seemingly related to sequencing, tend to be actually due to “limitations in attention, working memory, and/or conceptual knowledge“. Hence, instead of targeting sequencing abilities in therapy, SLPs should instead use contextualized language intervention to target aspects of narrative development (macro and microstructural elements). There you have it! Ten practical suggestions from Dr. Kamhi ready for immediate implementation! And for more information, I highly recommend reading the other articles in the same
There you have it! Ten practical suggestions from Dr. Kamhi ready for immediate implementation! And for more information, I highly recommend reading the other articles in the same 
 Richie is an engaging 9 year old boy, who attends therapy to improve his language skills. He is compliant and cooperative in sessions and is eager to learn new information. There’s only one problem, Richie is unable to spontaneously ask questions and request clarification when he doesn’t understand the presented information. Oh, he’ll sit there quietly, intently looking at the therapist and making perfect eye contact. His entire body posture will scream at you “I am listening to you and I value what you have to say!” But when it comes to answering questions about what he’s just learned, Richie clearly doesn’t get it and has no clue on how to obtain it! He might attempt to answer the questions and stumble half way through before giving up. He might also provide a response completely unrelated to the presented question. But most of the time, much to your frustration, Richie will simply shrug his shoulders and reply “I don’t know”. This is typically when many graduate speech interns and CFs alike will ask him with barely disguised frustration: “Why didn’t tell me before you didn’t understand?” Richie will shrug his shoulders again. Oh, he is not trying to be oppositional, he really doesn’t know!
Richie is an engaging 9 year old boy, who attends therapy to improve his language skills. He is compliant and cooperative in sessions and is eager to learn new information. There’s only one problem, Richie is unable to spontaneously ask questions and request clarification when he doesn’t understand the presented information. Oh, he’ll sit there quietly, intently looking at the therapist and making perfect eye contact. His entire body posture will scream at you “I am listening to you and I value what you have to say!” But when it comes to answering questions about what he’s just learned, Richie clearly doesn’t get it and has no clue on how to obtain it! He might attempt to answer the questions and stumble half way through before giving up. He might also provide a response completely unrelated to the presented question. But most of the time, much to your frustration, Richie will simply shrug his shoulders and reply “I don’t know”. This is typically when many graduate speech interns and CFs alike will ask him with barely disguised frustration: “Why didn’t tell me before you didn’t understand?” Richie will shrug his shoulders again. Oh, he is not trying to be oppositional, he really doesn’t know! 