 Today I am writing my last installment in the five-part early intervention assessment series. My previous posts on this topic included:
Today I am writing my last installment in the five-part early intervention assessment series. My previous posts on this topic included:
- General speech and language assessments of children under 3 years of age.
- Assessments of toddlers with suspected motor speech disorders
- Assessments of children ~16-18 months of age
- Assessments of Social Pragmatic Abilities of Children Under 3
Today I’d like to talk about the assessment of feeding abilities of children under 3 years of age. Just to be clear, in my post, I am not offering tips on the assessment of medically fragile or neurologically impaired children with complex swallowing and feeding disorders such as severe food selectivity. Rather, I am offering suggestions for routine orofacial and feeding assessments of young children with normal swallowing but slightly immature feeding abilities.
First, let take a look at what the typical feeding development looks like in children 0-3 years of age. For this, I really like to use a resource from Dr. Joan Arvedson entitled: Developmental milestones and feeding skills birth to 36 months from her article Swallowing and feeding in infants and young children which was published online in 2006.
| Age (months) | Development/posture | Feeding/oral sensorimotor |
| Source: Adapted from Arvedson and Brodsky (pp. 62–67). | ||
| Birth to 4–6 | Neck and trunk with balanced flexor and extensor tone Visual fixation and tracking Learning to control body against gravity Sitting with support near 6 months Rolling over Brings hands to mouth |
Nipple feeding, breast, or bottle Hand on bottle during feeding (2–4 months) Maintains semiflexed posture during feeding Promotion of infant–parent interaction |
| 6–9 (transition feeding) | Sitting independently for short time Self-oral stimulation (mouthing hands and toys) Extended reach with pincer grasp Visual interest in small objects Object permanence Stranger anxiety Crawling on belly, creeping on all fours |
Feeding more upright position Spoon feeding for thin, smooth puree Suckle pattern initially Suckle suck Both hands to hold bottle Finger feeding introduced Vertical munching of easily dissolvable solids Preference for parents to feed |
| 9–12 | Pulling to stand Cruising along furniture First steps by 12 months Assisting with spoon; some become independent Refining pincer grasp |
Cup drinking Eats lumpy, mashed food Finger feeding for easily dissolvable solids Chewing includes rotary jaw action |
| 12–18 | Refining all gross and fine motor skills Walking independently Climbing stairs Running Grasping and releasing with precision |
Self-feeding: grasps spoon with whole hand Holding cup with 2 hands Drinking with 4–5 consecutive swallows Holding and tipping bottle |
| >18–24 | Improving equilibrium with refinement of upper extremity coordination. Increasing attention and persistence in play activities Parallel or imitative play Independence from parents Using tools |
Swallowing with lip closure Self-feeding predominates Chewing broad range of food Up–down tongue movements precise |
| 24–36 | Refining skills Jumping in place Pedaling tricycle Using scissors |
Circulatory jaw rotations Chewing with lips closed One-handed cup holding and open cup drinking with no spilling Using fingers to fill spoon Eating wide range of solid food Total self-feeding, using fork |
Now, let’s discuss the importance of examining the child’s facial features and oral structures. During these examinations it is important to document anything out of the ordinary noted in the child’s facial features or oral cavity.
Facial dysmorphia, signs of asymmetry indicative of paresis, unusual spots, nodules, openings, growths, etc, all need to be documented. Note the condition of the child’s mouth. Is there excessive tooth decay? Do you see an unusual absence of teeth? Is there an unusual bite (open, cross, etc.), unusual voice or a cough, in the absence of a documented illness? Here’s an example from a write up on a 2-8-year-old male toddler, below:
Facial observations revealed dysmorphic features: microcephaly (small head circumference), anteriorly rotated ears (wide set), and medially deviated, inward set eyes. A presence of mild-moderate hypotonicity (low tone) of the face [and trunk] was also noted. FA presented with mostly closed mouth posture and appropriate oral postural control at rest but moderate drooling (drool fell on clothes vs. touching chin only) was noted during speech tasks and during play. It’s important to note that the latter might be primarily behavioral in origin since FA was also observed to engage in “drool play” – gathering oral secretions at lip level then slowly and deliberately expelling them in a thin stream from his mouth and onto his shirt.
Articulatory structures including lips, tongue, hard palate and velum appeared to be unremarkable and are adequate for speech purposes. FA’s dentition was adequate for speech purposes as well. Oral motor function was appropriate for lingual lateralization, labial retraction, volitional pucker and lingual elevation. Lingual depression was not achieved. Diadochokinesis for sequential and alternate movements was unremarkable. Overall, FA’s oral structures and function presented to be adequate for speech production purposes.
FA’s prosody, pitch, and loudness were within normal limits for age and gender. No clinical dysfluencies were present during the evaluation. Vocal quality was remarkable for intermittent hoarseness which tended to decrease (clear up) as speech output increased and may be largely due to a cold (he presented with a runny nose during the assessment). Vocal quality should continue to be monitored during therapy sessions for indications of persistent hoarseness in the absence of a cold.
From there I typically segue into a discussion of the child’s feeding and swallowing abilities. Below is an excerpt discussing the strengths and needs of an 18-month-old internationally adopted female.
“During the assessment concerns presented regarding AK’s feeding abilities only. No swallowing concerns were reported or observed during the assessment. As per the parental report, at the age of 18 months, AK is still drinking from the bottle and consuming only puréed foods, which is significantly delayed for a child her age. AK’s feeding skills were assessed at snack time via indirect observation and select direct food administration. The following foods and liquids were presented to AK during the assessment: 2 oz of yogurt, 18 cheerios, 4 banana and 2 apple bites, and 40 ml of water (via cup and straw). AK was observed to accept all of the above foods and liquids readily when offered.
Spoon Stripping and Mouth Closure: During the yogurt presentation, AK’s spoon stripping abilities and mouth closure were deemed good (adequate) when fed by a caregiver and fair when AK fed self (incomplete food stripping from the spoon was observed due to only partial mouth closure). According to parental report, AK’s spoon stripping abilities have improved in recent months. Ms. K was observed to present spoon upwardly in AK’s mouth and hold it still until AK placed her lips firmly around the spoon and initiated spoon stripping. Since this strategy is working adequately for all parties in question no further recommendations regarding spoon feeding are necessary at this time. Skill monitoring is recommended on an ongoing basis for further refinement.
Biting and Chewing Abilities on Solids and Semi-Solids: AK’s chewing abilities were judged to be immature at this time for both solid (e.g., Cheerios) and semi-solid foods (e.g., banana). AK was observed to feed self Cheerios from a plate (1 at a time). She placed a cheerio laterally on lower right molars and attempted to grind it. When the cheerio was presented to AK midline she was observed to anteriorly munch it, or mash it against the hard palate. Notably, when too many cheerios were presented to her, rather than grasping and consuming them AK began to bang on a plate with both hands and throw the cheerios around the room.
During feeding, the most difficulty was observed with biting and chewing solid and semisolid fruit (e.g., apple and banana pieces). When presented with a banana, AK manifested moderate difficulties biting off an adequately sized piece (she bit off too much). Consequently, due to the fact that she was unable to adequately chew on a piece that large, manual extraction of food from the oral cavity was initiated due to choking concerns. It is important to note that during all food presentations AK did not display a diagonal rotary chew, which is below age expectancy for a child her age. Feeding strengths noted during today’s assessment included complete mouth closure (including lack of drooling and anterior food loss) during assisted spoon and finger foods feeding.
Cup and Straw Drinking: AK was also observed to drink 40 mls of water from a cup given parental assistance. Minor anterior spillage was intermittently noted during liquid intake. It is recommended that the parents modify cup presentation by providing AK with a plastic cup with two handles on each side, which would improve her ability to grasp and maintain hold on cup while drinking.
Straw drinking trials were attempted during the assessment as it is a skill which typically emerges between 8-9 months of age and solidifies around 12-13 months of age (Hunt et al, 2000). When AK was presented with a shortened straw placed in cup, she was initially able to create enough intraoral pressure to suck in a small amount of liquid. However, AK quickly lost the momentum and began to tentatively chew on the presented straw as which point the trial was discontinued.
Based on the feeding assessment AK presented with mildly decreased abilities in the oral phase of feeding. It is recommended that she receive feeding therapy with a focus on refining her feeding abilities.”
I follow the above, with a summary of evaluation impressions, recommendations, as well as suggested therapy goals. Finally, I conclude my report with a statement regarding the child’s prognosis (e.g., excellent, good, fair, etc.) as well as list potential maintaining factors affecting the duration of therapy provision.
So what about you? How do you assess the feeding and swallowing of abilities of children under 3 on your caseload? What foods, tasks, and procedures do you use?
 Back in late February I did a guest post for Teach Speech 365. In case you missed it I am running it again on my blog since spring is now in full bloom!
Back in late February I did a guest post for Teach Speech 365. In case you missed it I am running it again on my blog since spring is now in full bloom! Over the years this blog has amassed many posts on a variety of topics pertaining to the assessment and treatment in speech-language pathology. With over 300 posts and over 130 search categories it’s no wonder that some of you have reached out to ask about effective ways of finding relevant information quickly. As such, in addition to the existing categories pertaining to specific topics (e.g., writing, social communication, etc.) I have created two specific categories which were asked about by numerous blog subscribers in recent emails.
Over the years this blog has amassed many posts on a variety of topics pertaining to the assessment and treatment in speech-language pathology. With over 300 posts and over 130 search categories it’s no wonder that some of you have reached out to ask about effective ways of finding relevant information quickly. As such, in addition to the existing categories pertaining to specific topics (e.g., writing, social communication, etc.) I have created two specific categories which were asked about by numerous blog subscribers in recent emails.  The following is an informational post on the disease SMA (spinal muscle atrophy) by Rose Ann Kesting M.A. CCC-SLP. After reading, please
The following is an informational post on the disease SMA (spinal muscle atrophy) by Rose Ann Kesting M.A. CCC-SLP. After reading, please  I’ve been meaning to write this post for some time and have finally decided to do it now due to an increased prevalence of “non-traditional” treatment options available to parents of language impaired children.
I’ve been meaning to write this post for some time and have finally decided to do it now due to an increased prevalence of “non-traditional” treatment options available to parents of language impaired children.







 There you have it: that’s what the harm is! The toll of these quack practices can be very significant and can go far beyond the financial. So the next time someone utters the statement: “What’s the Harm in That?” consider the above information in order to make the informed decisions regarding the treatment for the most vulnerable parties involved: the children in your care!
There you have it: that’s what the harm is! The toll of these quack practices can be very significant and can go far beyond the financial. So the next time someone utters the statement: “What’s the Harm in That?” consider the above information in order to make the informed decisions regarding the treatment for the most vulnerable parties involved: the children in your care!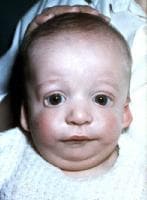 Today’s guest post on genetic syndromes comes from Amy Locy, who is contributing an informative piece on the Treacher Collins Syndrome (TCS). TSC occurs in 1 out of every 50,000 live births with 40% of children born with TCS having a family member with the syndrome. TCS is distributed equally across genders and races. It can often occur in conjunction with the Pierre Robin Sequence.
Today’s guest post on genetic syndromes comes from Amy Locy, who is contributing an informative piece on the Treacher Collins Syndrome (TCS). TSC occurs in 1 out of every 50,000 live births with 40% of children born with TCS having a family member with the syndrome. TCS is distributed equally across genders and races. It can often occur in conjunction with the Pierre Robin Sequence.  In this day and age, in addition to speech language assessment and intervention, many speech language pathologists are engaged in a number of enterprising endeavors ranging from creating and selling therapeutic materials to public speaking and presenting. As a result of these activities we continuously create numerous digital downloads for primary (e.g., TPT materials) and secondary (handouts to accompany presentations) customer consumption. Of course in these materials we specify exactly how we want them to be used. Typically we place a number of disclaimers on the front page including: “Do Not Copy”, “Do Not Resell”, “For Individual Use Only”, “Do not remove copyright” and so on. But what happens if these disclaimers are disregarded and you find the product you had worked so hard on for a period of days, weeks or even months, publicly posted on an ebook search engine website for all to see and download.
In this day and age, in addition to speech language assessment and intervention, many speech language pathologists are engaged in a number of enterprising endeavors ranging from creating and selling therapeutic materials to public speaking and presenting. As a result of these activities we continuously create numerous digital downloads for primary (e.g., TPT materials) and secondary (handouts to accompany presentations) customer consumption. Of course in these materials we specify exactly how we want them to be used. Typically we place a number of disclaimers on the front page including: “Do Not Copy”, “Do Not Resell”, “For Individual Use Only”, “Do not remove copyright” and so on. But what happens if these disclaimers are disregarded and you find the product you had worked so hard on for a period of days, weeks or even months, publicly posted on an ebook search engine website for all to see and download.  A few weeks ago I received my new gleaming set of Speech Buddies for the purposes of review. So today I’ll be describing my experiences using speech buddies in speech therapy with several clients. My client’s ages were 3.5, 4.5, 8, and 9. Prior to initiating the use of the speech buddies I have posed a number of questions for myself including:
A few weeks ago I received my new gleaming set of Speech Buddies for the purposes of review. So today I’ll be describing my experiences using speech buddies in speech therapy with several clients. My client’s ages were 3.5, 4.5, 8, and 9. Prior to initiating the use of the speech buddies I have posed a number of questions for myself including:
 Wait a second, you might say! “Isn’t that a definition of ‘code-switching’?” And the answer is: “No!” The concept of ‘code-switching’ implies that bilinguals use two separate linguistic codes which do not overlap/reference each other. In contrast, ‘translanguaging’ assumes from the get-go that “bilinguals have one linguistic repertoire from which they select features strategically to communicate effectively” (Garcia, 2012, pg. 1). Bilinguals engage in translanguaging on an ongoing basis in their daily lives. They speak different languages to different individuals, find ‘Google’ translations of words and compare results from various online sites, listen to music in one language but watch TV in another, as well as watch TV announcers fluidly integrate several languages in their event narratives during news or in infomercials (Celic & Seltzer, 2011). For functional bilinguals, these practices are such integral part of their daily lives that they rarely realize just how much ‘translanguaging’ they actually do every day.
Wait a second, you might say! “Isn’t that a definition of ‘code-switching’?” And the answer is: “No!” The concept of ‘code-switching’ implies that bilinguals use two separate linguistic codes which do not overlap/reference each other. In contrast, ‘translanguaging’ assumes from the get-go that “bilinguals have one linguistic repertoire from which they select features strategically to communicate effectively” (Garcia, 2012, pg. 1). Bilinguals engage in translanguaging on an ongoing basis in their daily lives. They speak different languages to different individuals, find ‘Google’ translations of words and compare results from various online sites, listen to music in one language but watch TV in another, as well as watch TV announcers fluidly integrate several languages in their event narratives during news or in infomercials (Celic & Seltzer, 2011). For functional bilinguals, these practices are such integral part of their daily lives that they rarely realize just how much ‘translanguaging’ they actually do every day. One of the most useful features of translanguaging (and there are many) is that it assists with further development of bilinguals’ metalinguistic awareness abilities by allowing them to compare language practices as well as explicitly notice language features. Consequently, not only do speech-language pathologists (SLPs) need to be aware of translanguaging when working with culturally diverse clients, they can actually assist their clients make greater linguistic gains by embracing translanguaging practices. Furthermore, one does not have to be a bilingual SLP to incorporate translanguaging practices in the therapy room. Monolingual SLPs can certainly do it as well, and with a great degree of success.
One of the most useful features of translanguaging (and there are many) is that it assists with further development of bilinguals’ metalinguistic awareness abilities by allowing them to compare language practices as well as explicitly notice language features. Consequently, not only do speech-language pathologists (SLPs) need to be aware of translanguaging when working with culturally diverse clients, they can actually assist their clients make greater linguistic gains by embracing translanguaging practices. Furthermore, one does not have to be a bilingual SLP to incorporate translanguaging practices in the therapy room. Monolingual SLPs can certainly do it as well, and with a great degree of success. Here are some strategies of how this can be accomplished. Let us begin with bilingual SLPs who have the ability to do therapy in both languages. One great way to incorporate translanguaging in therapy is to alternate between English and the desired language (e.g., Spanish) throughout the session. Translanguaging strategies may include: using key vocabulary, grammar and syntax structures in both languages (side to side), alternating between English and Spanish websites when researching specific information (e.g., an animal habitats, etc.), asking students to take notes in both languages or combining two languages in one piece of writing. For younger preschool students, reading the same book, translated in another language is also a viable option as it increases their lexicon in both languages.
Here are some strategies of how this can be accomplished. Let us begin with bilingual SLPs who have the ability to do therapy in both languages. One great way to incorporate translanguaging in therapy is to alternate between English and the desired language (e.g., Spanish) throughout the session. Translanguaging strategies may include: using key vocabulary, grammar and syntax structures in both languages (side to side), alternating between English and Spanish websites when researching specific information (e.g., an animal habitats, etc.), asking students to take notes in both languages or combining two languages in one piece of writing. For younger preschool students, reading the same book, translated in another language is also a viable option as it increases their lexicon in both languages. Those SLPs who treat ESL students with language disorders and collaborate with ESL teachers can design thematic intervention with a focus on particular topics of interest. For example, during the month of April there’s increased attention on the topic of ‘human impact on the environment.’ Students can read texts on this topic in English and then use the internet to look up websites containing the information in their birth language. They can also listen to a translation or a summary of the English book in their birth language. Finally, they can make comparisons of human impact on the environment between United States and their birth/heritage countries.
Those SLPs who treat ESL students with language disorders and collaborate with ESL teachers can design thematic intervention with a focus on particular topics of interest. For example, during the month of April there’s increased attention on the topic of ‘human impact on the environment.’ Students can read texts on this topic in English and then use the internet to look up websites containing the information in their birth language. They can also listen to a translation or a summary of the English book in their birth language. Finally, they can make comparisons of human impact on the environment between United States and their birth/heritage countries.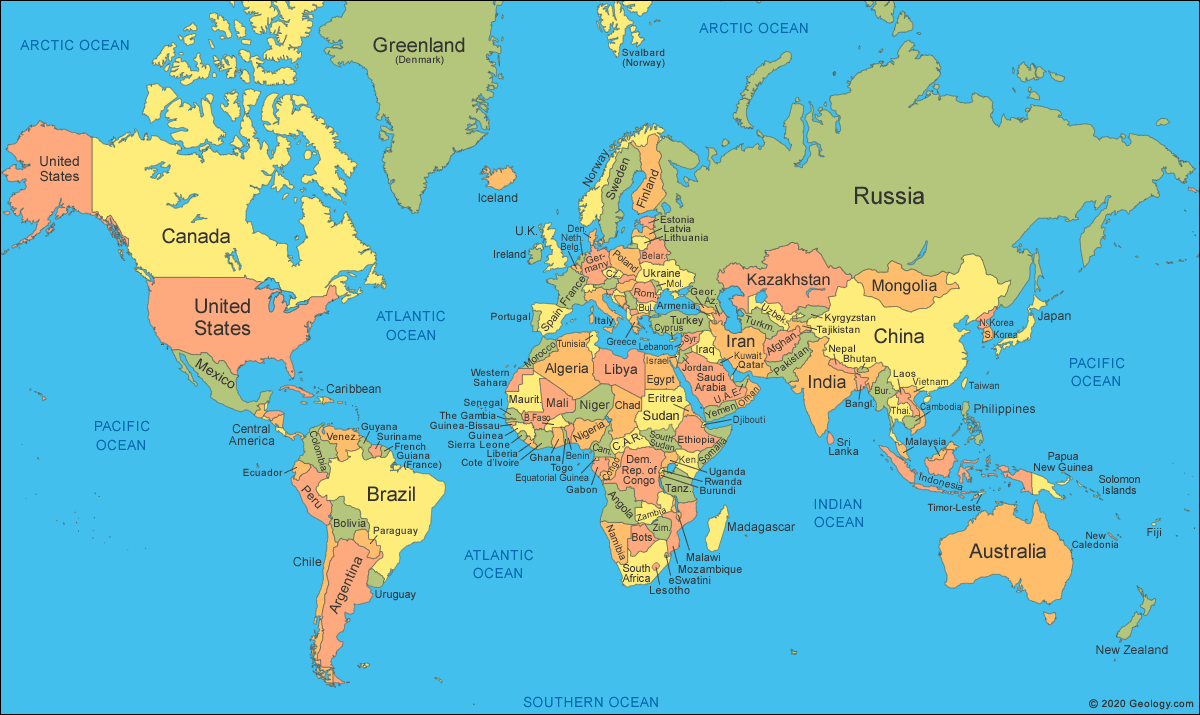 We can “Get to know our students” by displaying a world map in our therapy room/classroom and asking them to show us where they were born or came from (or where their family is from). We can label the map with our students’ names and photographs and provide them with the opportunity to discuss their culture and develop cultural connections. We can create a multilingual therapy room by using multilingual labels and word walls as well as sprinkling our English language therapy with words relevant to the students from their birth/heritage languages (e.g., songs and greetings, etc.).
We can “Get to know our students” by displaying a world map in our therapy room/classroom and asking them to show us where they were born or came from (or where their family is from). We can label the map with our students’ names and photographs and provide them with the opportunity to discuss their culture and develop cultural connections. We can create a multilingual therapy room by using multilingual labels and word walls as well as sprinkling our English language therapy with words relevant to the students from their birth/heritage languages (e.g., songs and greetings, etc.).