 Scenario: Len is a 7-2-year-old, 2nd-grade student who struggles with reading and writing in the classroom. He is very bright and has a high average IQ, yet when he is speaking he frequently can’t get his point across to others due to excessive linguistic reformulations and word-finding difficulties. The problem is that Len passed all the typical educational and language testing with flying colors, receiving average scores across the board on various tests including the Woodcock-Johnson Fourth Edition (WJ-IV) and the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-5 (CELF-5). Stranger still is the fact that he aced Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing, Second Edition (CTOPP-2), with flying colors, so he is not even eligible for a “dyslexia” diagnosis. Len is clearly struggling in the classroom with coherently expressing self, telling stories, understanding what he is reading, as well as putting his thoughts on paper. His parents have compiled impressively huge folders containing examples of his struggles. Yet because of his performance on the basic standardized assessment batteries, Len does not qualify for any functional assistance in the school setting, despite being virtually functionally illiterate in second grade.
Scenario: Len is a 7-2-year-old, 2nd-grade student who struggles with reading and writing in the classroom. He is very bright and has a high average IQ, yet when he is speaking he frequently can’t get his point across to others due to excessive linguistic reformulations and word-finding difficulties. The problem is that Len passed all the typical educational and language testing with flying colors, receiving average scores across the board on various tests including the Woodcock-Johnson Fourth Edition (WJ-IV) and the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-5 (CELF-5). Stranger still is the fact that he aced Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing, Second Edition (CTOPP-2), with flying colors, so he is not even eligible for a “dyslexia” diagnosis. Len is clearly struggling in the classroom with coherently expressing self, telling stories, understanding what he is reading, as well as putting his thoughts on paper. His parents have compiled impressively huge folders containing examples of his struggles. Yet because of his performance on the basic standardized assessment batteries, Len does not qualify for any functional assistance in the school setting, despite being virtually functionally illiterate in second grade.
The truth is that Len is quite a familiar figure to many SLPs, who at one time or another have encountered such a student and asked for guidance regarding the appropriate accommodations and services for him on various SLP-geared social media forums. But what makes Len such an enigma, one may inquire? Surely if the child had tangible deficits, wouldn’t standardized testing at least partially reveal them?
Well, it all depends really, on what type of testing was administered to Len in the first place. A few years ago I wrote a post entitled: “What Research Shows About the Functional Relevance of Standardized Language Tests“. What researchers found is that there is a “lack of a correlation between frequency of test use and test accuracy, measured both in terms of sensitivity/specificity and mean difference scores” (Betz et al, 2012, 141). Furthermore, they also found that the most frequently used tests were the comprehensive assessments including the Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals and the Preschool Language Scale as well as one-word vocabulary tests such as the Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test”. Most damaging finding was the fact that: “frequently SLPs did not follow up the comprehensive standardized testing with domain-specific assessments (critical thinking, social communication, etc.) but instead used the vocabulary testing as a second measure”.(Betz et al, 2012, 140)
In other words, many SLPs only use the tests at hand rather than the RIGHT tests aimed at identifying the student’s specific deficits. But the problem doesn’t actually stop there. Due to the variation in psychometric properties of various tests, many children with language impairment are overlooked by standardized tests by receiving scores within the average range or not receiving low enough scores to qualify for services.
Thus, “the clinical consequence is that a child who truly has a language impairment has a roughly equal chance of being correctly or incorrectly identified, depending on the test that he or she is given.” Furthermore, “even if a child is diagnosed accurately as language impaired at one point in time, future diagnoses may lead to the false perception that the child has recovered, depending on the test(s) that he or she has been given (Spaulding, Plante & Farinella, 2006, 69).”
There’s of course yet another factor affecting our hypothetical client and that is his relatively young age. This is especially evident with many educational and language testing for children in the 5-7 age group. Because the bar is set so low, concept-wise for these age-groups, many children with moderate language and literacy deficits can pass these tests with flying colors, only to be flagged by them literally two years later and be identified with deficits, far too late in the game. Coupled with the fact that many SLPs do not utilize non-standardized measures to supplement their assessments, Len is in a pretty serious predicament.
But what if there was a do-over? What could we do differently for Len to rectify this situation? For starters, we need to pay careful attention to his deficits profile in order to choose appropriate tests to evaluate his areas of needs. The above can be accomplished via a number of ways. The SLP can interview Len’s teacher and his caregiver/s in order to obtain a summary of his pressing deficits. Depending on the extent of the reported deficits the SLP can also provide them with a referral checklist to mark off the most significant areas of need.
In Len’s case, we already have a pretty good idea regarding what’s going on. We know that he passed basic language and educational testing, so in the words of Dr. Geraldine Wallach, we need to keep “peeling the onion” via the administration of more sensitive tests to tap into Len’s reported areas of deficits which include: word-retrieval, narrative production, as well as reading and writing.
 For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy (TILLS), which was developed to identify language and literacy disorders, has good psychometric properties, and contains subtests for assessment of relevant skills such as reading fluency, reading comprehension, phonological awareness, spelling, as well as writing in school-age children.
For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the Test of Integrated Language and Literacy (TILLS), which was developed to identify language and literacy disorders, has good psychometric properties, and contains subtests for assessment of relevant skills such as reading fluency, reading comprehension, phonological awareness, spelling, as well as writing in school-age children.
 Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the Social Language Development Test Elementary (SLDTE). Here’s why. Research indicates that narrative weaknesses significantly correlate with social communication deficits (Norbury, Gemmell & Paul, 2014). As such, it’s not just children with Autism Spectrum Disorders who present with impaired narrative abilities. Many children with developmental language impairment (DLD) (#devlangdis) can present with significant narrative deficits affecting their social and academic functioning, which means that their social communication abilities need to be tested to confirm/rule out presence of these difficulties.
Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the Social Language Development Test Elementary (SLDTE). Here’s why. Research indicates that narrative weaknesses significantly correlate with social communication deficits (Norbury, Gemmell & Paul, 2014). As such, it’s not just children with Autism Spectrum Disorders who present with impaired narrative abilities. Many children with developmental language impairment (DLD) (#devlangdis) can present with significant narrative deficits affecting their social and academic functioning, which means that their social communication abilities need to be tested to confirm/rule out presence of these difficulties.
However, standardized tests are not enough, since even the best-standardized tests have significant limitations. As such, several non-standardized assessments in the areas of narrative production, reading, and writing, may be recommended for Len to meaningfully supplement his testing.
Let’s begin with an informal narrative assessment which provides detailed information regarding microstructural and macrostructural aspects of storytelling as well as child’s thought processes and socio-emotional functioning. My nonstandardized narrative assessments are based on the book elicitation recommendations from the SALT website. For 2nd graders, I use the book by Helen Lester entitled Pookins Gets Her Way. I first read the story to the child, then cover up the words and ask the child to retell the story based on pictures. I read the story first because: “the model narrative presents the events, plot structure, and words that the narrator is to retell, which allows more reliable scoring than a generated story that can go in many directions” (Allen et al, 2012, p. 207).
As the child is retelling his story I digitally record him using the Voice Memos application on my iPhone, for a later transcription and thorough analysis. During storytelling, I only use the prompts: ‘What else can you tell me?’ and ‘Can you tell me more?’ to elicit additional information. I try not to prompt the child excessively since I am interested in cataloging all of his narrative-based deficits. After I transcribe the sample, I analyze it and make sure that I include the transcription and a detailed write-up in the body of my report, so parents and professionals can see and understand the nature of the child’s errors/weaknesses.
 Now we are ready to move on to a brief nonstandardized reading assessment. For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled: Reading for Comprehension, which contains books for grades 1-8. After I confirm with either the parent or the child’s teacher that the selected passage is reflective of the complexity of work presented in the classroom for his grade level, I ask the child to read the text. As the child is reading, I calculate the correct number of words he reads per minute as well as what type of errors the child is exhibiting during reading. Then I ask the child to state the main idea of the text, summarize its key points as well as define select text embedded vocabulary words and answer a few, verbally presented reading comprehension questions. After that, I provide the child with accompanying 5 multiple choice question worksheet and ask the child to complete it. I analyze my results in order to determine whether I have accurately captured the child’s reading profile.
Now we are ready to move on to a brief nonstandardized reading assessment. For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled: Reading for Comprehension, which contains books for grades 1-8. After I confirm with either the parent or the child’s teacher that the selected passage is reflective of the complexity of work presented in the classroom for his grade level, I ask the child to read the text. As the child is reading, I calculate the correct number of words he reads per minute as well as what type of errors the child is exhibiting during reading. Then I ask the child to state the main idea of the text, summarize its key points as well as define select text embedded vocabulary words and answer a few, verbally presented reading comprehension questions. After that, I provide the child with accompanying 5 multiple choice question worksheet and ask the child to complete it. I analyze my results in order to determine whether I have accurately captured the child’s reading profile.
Finally, if any additional information is needed, I administer a nonstandardized writing assessment, which I base on the Common Core State Standards for 2nd grade. For this task, I provide a student with a writing prompt common for second grade and give him a period of 15-20 minutes to generate a writing sample. I then analyze the writing sample with respect to contextual conventions (punctuation, capitalization, grammar, and syntax) as well as story composition (overall coherence and cohesion of the written sample).
The above relatively short assessment battery (2 standardized tests and 3 informal assessment tasks) which takes approximately 2-2.5 hours to administer, allows me to create a comprehensive profile of the child’s language and literacy strengths and needs. It also allows me to generate targeted goals in order to begin effective and meaningful remediation of the child’s deficits.
Children like Len will, unfortunately, remain unidentified unless they are administered more sensitive tasks to better understand their subtle pattern of deficits. Consequently, to ensure that they do not fall through the cracks of our educational system due to misguided overreliance on a limited number of standardized assessments, it is very important that professionals select the right assessments, rather than the assessments at hand, in order to accurately determine the child’s areas of needs.
References:
- Allen, M, Ukrainetz, T & Carswell, A (2012) The narrative language performance of three types of at-risk first-grade readers. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 43(2), 205-221.
- Betz et al. (2013) Factors Influencing the Selection of Standardized Tests for the Diagnosis of Specific Language Impairment. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 44, 133-146.
- Hasbrouck, J. & Tindal, G. A. (2006). Oral reading fluency norms: A valuable assessment tool for reading teachers. The Reading Teacher. 59(7), 636-644.).
- Norbury, C. F., Gemmell, T., & Paul, R. (2014). Pragmatics abilities in narrative production: a cross-disorder comparison. Journal of child language, 41(03), 485-510.
- Peña, E.D., Spaulding, T.J., & Plante, E. (2006). The Composition of Normative Groups and Diagnostic Decision Making: Shooting Ourselves in the Foot. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 15, 247-254.
- Spaulding, Plante & Farinella (2006) Eligibility Criteria for Language Impairment: Is the Low End of Normal Always Appropriate? Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 37, 61-72.
- Spaulding, Szulga, & Figueria (2012) Using Norm-Referenced Tests to Determine Severity of Language Impairment in Children: Disconnect Between U.S. Policy Makers and Test Developers. Journal of Speech, Language and Hearing Research. 43, 176-190.
 Two years ago I wrote a blog post entitled: “
Two years ago I wrote a blog post entitled: “
 First up is the concept of learning vs. generalization. Here Dr. Kamhi discusses that some clinicians still possess an “outdated behavioral view of learning” in our field, which is not theoretically and clinically useful. He explains that when we are talking about generalization – what children truly have a difficulty with is “transferring narrow limited rules to new situations“. “Children with language and learning problems will have difficulty acquiring broad-based rules and modifying these rules once acquired, and they also will be more vulnerable to performance demands on speech production and comprehension (Kamhi, 1988)” (93). After all, it is not “reasonable to expect children to use language targets consistently after a brief period of intervention” and while we hope that “language intervention [is] designed to lead children with language disorders to acquire broad-based language rules” it is a hugely difficult task to undertake and execute.
First up is the concept of learning vs. generalization. Here Dr. Kamhi discusses that some clinicians still possess an “outdated behavioral view of learning” in our field, which is not theoretically and clinically useful. He explains that when we are talking about generalization – what children truly have a difficulty with is “transferring narrow limited rules to new situations“. “Children with language and learning problems will have difficulty acquiring broad-based rules and modifying these rules once acquired, and they also will be more vulnerable to performance demands on speech production and comprehension (Kamhi, 1988)” (93). After all, it is not “reasonable to expect children to use language targets consistently after a brief period of intervention” and while we hope that “language intervention [is] designed to lead children with language disorders to acquire broad-based language rules” it is a hugely difficult task to undertake and execute.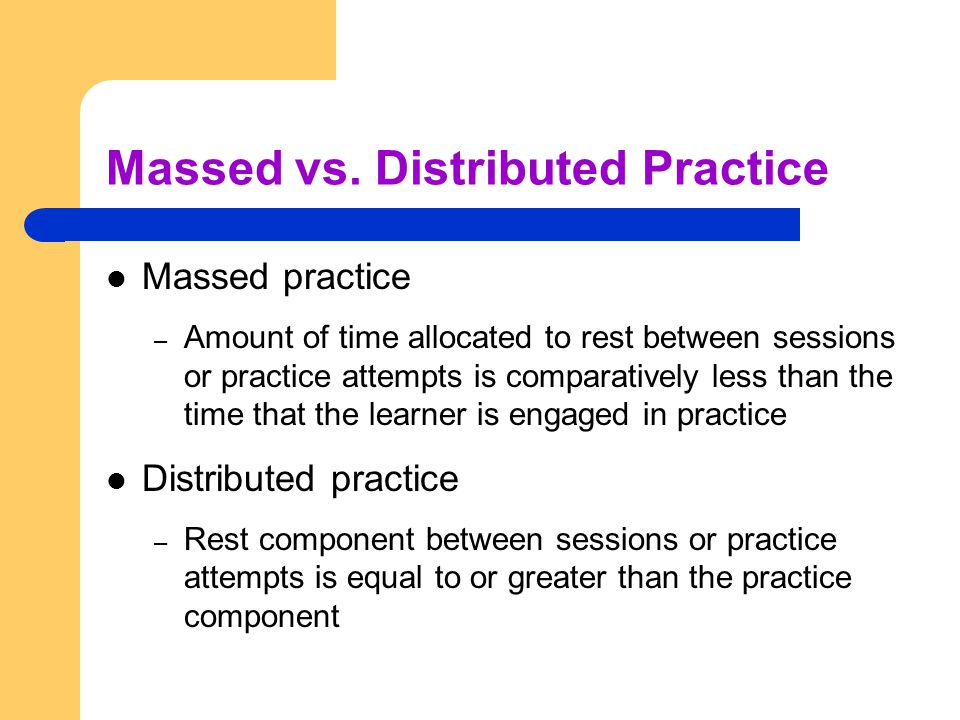 After that, Dr. Kamhi addresses the concept of distributed practice (spacing of intervention) and how important it is for teaching children with language disorders. He points out that a number of recent studies have found that “spacing and distribution of teaching episodes have more of an impact on treatment outcomes than
After that, Dr. Kamhi addresses the concept of distributed practice (spacing of intervention) and how important it is for teaching children with language disorders. He points out that a number of recent studies have found that “spacing and distribution of teaching episodes have more of an impact on treatment outcomes than 
 From there lets us take a look at Dr. Kamhi’s recommendations for grammar and syntax. Grammatical development goes much further than addressing Brown’s morphemes in therapy and calling it a day. As such, it is important to understand that children with developmental language disorders (DLD) (#DevLang) do not have difficulty acquiring all morphemes. Rather studies have shown that they have difficulty learning grammatical morphemes that reflect tense and agreement (e.g., third-person singular, past tense, auxiliaries, copulas, etc.). As such, use of measures developed by
From there lets us take a look at Dr. Kamhi’s recommendations for grammar and syntax. Grammatical development goes much further than addressing Brown’s morphemes in therapy and calling it a day. As such, it is important to understand that children with developmental language disorders (DLD) (#DevLang) do not have difficulty acquiring all morphemes. Rather studies have shown that they have difficulty learning grammatical morphemes that reflect tense and agreement (e.g., third-person singular, past tense, auxiliaries, copulas, etc.). As such, use of measures developed by  Dr. Kamhi supports the above point by providing an example of two passages. One, which describes a random order of events, and another which follows a logical order of events. He then points out that the randomly ordered story relies exclusively on attention and memory in terms of “sequencing”, while the second story reduces demands on memory due to its logical flow of events. As such, he points out that retelling deficits seemingly related to sequencing, tend to be actually due to “limitations in attention, working memory, and/or conceptual knowledge“. Hence, instead of targeting sequencing abilities in therapy, SLPs should instead use contextualized language intervention to target aspects of narrative development (macro and microstructural elements).
Dr. Kamhi supports the above point by providing an example of two passages. One, which describes a random order of events, and another which follows a logical order of events. He then points out that the randomly ordered story relies exclusively on attention and memory in terms of “sequencing”, while the second story reduces demands on memory due to its logical flow of events. As such, he points out that retelling deficits seemingly related to sequencing, tend to be actually due to “limitations in attention, working memory, and/or conceptual knowledge“. Hence, instead of targeting sequencing abilities in therapy, SLPs should instead use contextualized language intervention to target aspects of narrative development (macro and microstructural elements). There you have it! Ten practical suggestions from Dr. Kamhi ready for immediate implementation! And for more information, I highly recommend reading the other articles in the same
There you have it! Ten practical suggestions from Dr. Kamhi ready for immediate implementation! And for more information, I highly recommend reading the other articles in the same  I’ve always loved fairy tales! Much like Audrey Hepburn “If I’m honest I have to tell you I still read fairy-tales and I like them best of all.” Not to compare myself with Einstein (sadly in any way, sigh) but “When I examine myself and my methods of thought, I come to the conclusion that the gift of fantasy has meant more to me than any talent for abstract, positive thinking.”
I’ve always loved fairy tales! Much like Audrey Hepburn “If I’m honest I have to tell you I still read fairy-tales and I like them best of all.” Not to compare myself with Einstein (sadly in any way, sigh) but “When I examine myself and my methods of thought, I come to the conclusion that the gift of fantasy has meant more to me than any talent for abstract, positive thinking.” Today I want to talk treatment. That thing that we need to plan for as we are doing our assessments. But are we starting our treatments the right way? The answer may surprise you. I often see SLPs phrasing questions regarding treatment the following way: “I have a student diagnosed with ____ (insert disorder here). What is everyone using (program/app/materials) during therapy sessions to address ___ diagnosis?”
Today I want to talk treatment. That thing that we need to plan for as we are doing our assessments. But are we starting our treatments the right way? The answer may surprise you. I often see SLPs phrasing questions regarding treatment the following way: “I have a student diagnosed with ____ (insert disorder here). What is everyone using (program/app/materials) during therapy sessions to address ___ diagnosis?” There could be endless variations of how deficits manifest in poor readers. Is it aspects of phonological awareness, phonics, morphology, etc. What combination of deficits is preventing the child from becoming a good reader?
There could be endless variations of how deficits manifest in poor readers. Is it aspects of phonological awareness, phonics, morphology, etc. What combination of deficits is preventing the child from becoming a good reader? Reading Fluency: “LG’s reading fluency during this task was judged to be significantly affected by excessive speed, inappropriate pausing, word misreadings, choppy prosody, as well as inefficient word attack skills. While she was able to limitedly utilize the phonetic spelling of unfamiliar words (e.g., __) provided to her in parenthesis next to the word (which she initially misread as ‘__’), she exhibited limited use of metalinguistic strategies (e.g., pre-scanning sentences to aid text comprehension, self-correcting to ensure that the read words made sense in the context of the sentence, etc.), when reading the provided passage. To illustrate, during the reading of the text, LG was observed to frequently (at least 3 times) lose her place and skip entire lines of text without any attempts at self-correction. At times she was observed to read the same word a number of different ways (e.g., read ‘soup’ as ‘soup’ then as ‘soap’, ‘roots’ as ‘roofs’ then as ‘roots’, etc.) without attempting to self-correct. LG’s oral reading rate was also observed to be impaired for her age/grade levels. Her prosody was significantly adversely affected due to lack of adequate pausing for punctuation marks (e.g., periods, commas, etc.). Instead, she paused during text reading only when he could not decode select words in the text. Though, LG was able to read 70 words per minute, which was judged to be grossly commensurate with grade-level, out of these 70 words she skipped 2 entire lines of text, invented an entire line of text, as well as made 4 decoding errors and 6 inappropriate pauses.”
Reading Fluency: “LG’s reading fluency during this task was judged to be significantly affected by excessive speed, inappropriate pausing, word misreadings, choppy prosody, as well as inefficient word attack skills. While she was able to limitedly utilize the phonetic spelling of unfamiliar words (e.g., __) provided to her in parenthesis next to the word (which she initially misread as ‘__’), she exhibited limited use of metalinguistic strategies (e.g., pre-scanning sentences to aid text comprehension, self-correcting to ensure that the read words made sense in the context of the sentence, etc.), when reading the provided passage. To illustrate, during the reading of the text, LG was observed to frequently (at least 3 times) lose her place and skip entire lines of text without any attempts at self-correction. At times she was observed to read the same word a number of different ways (e.g., read ‘soup’ as ‘soup’ then as ‘soap’, ‘roots’ as ‘roofs’ then as ‘roots’, etc.) without attempting to self-correct. LG’s oral reading rate was also observed to be impaired for her age/grade levels. Her prosody was significantly adversely affected due to lack of adequate pausing for punctuation marks (e.g., periods, commas, etc.). Instead, she paused during text reading only when he could not decode select words in the text. Though, LG was able to read 70 words per minute, which was judged to be grossly commensurate with grade-level, out of these 70 words she skipped 2 entire lines of text, invented an entire line of text, as well as made 4 decoding errors and 6 inappropriate pauses.”
 So you’ve completed a thorough evaluation of your student’s speech and language abilities and are in the process of creating goals and objectives to target in sessions. The problem is that many of the students on our caseloads present with pervasive deficits in many areas of language.
So you’ve completed a thorough evaluation of your student’s speech and language abilities and are in the process of creating goals and objectives to target in sessions. The problem is that many of the students on our caseloads present with pervasive deficits in many areas of language.





 Today I am writing my last installment in the five-part early intervention assessment series. My
Today I am writing my last installment in the five-part early intervention assessment series. My 
 Spoon Stripping and Mouth Closure: During the yogurt presentation, AK’s spoon stripping abilities and mouth closure were deemed good (adequate) when fed by a caregiver and fair when AK fed self (incomplete food stripping from the spoon was observed due to only partial mouth closure). According to parental report, AK’s spoon stripping abilities have improved in recent months. Ms. K was observed to present spoon upwardly in AK’s mouth and hold it still until AK placed her lips firmly around the spoon and initiated spoon stripping. Since this strategy is working adequately for all parties in question no further recommendations regarding spoon feeding are necessary at this time. Skill monitoring is recommended on an ongoing basis for further refinement.
Spoon Stripping and Mouth Closure: During the yogurt presentation, AK’s spoon stripping abilities and mouth closure were deemed good (adequate) when fed by a caregiver and fair when AK fed self (incomplete food stripping from the spoon was observed due to only partial mouth closure). According to parental report, AK’s spoon stripping abilities have improved in recent months. Ms. K was observed to present spoon upwardly in AK’s mouth and hold it still until AK placed her lips firmly around the spoon and initiated spoon stripping. Since this strategy is working adequately for all parties in question no further recommendations regarding spoon feeding are necessary at this time. Skill monitoring is recommended on an ongoing basis for further refinement.  Cup and Straw Drinking: AK was also observed to drink 40 mls of water from a cup given parental assistance. Minor anterior spillage was intermittently noted during liquid intake. It is recommended that the parents modify cup presentation by providing AK with a plastic cup with two handles on each side, which would improve her ability to grasp and maintain hold on cup while drinking.
Cup and Straw Drinking: AK was also observed to drink 40 mls of water from a cup given parental assistance. Minor anterior spillage was intermittently noted during liquid intake. It is recommended that the parents modify cup presentation by providing AK with a plastic cup with two handles on each side, which would improve her ability to grasp and maintain hold on cup while drinking. In the past several years, due to an influx of adolescent students with language and learning difficulties on my caseload, I have begun to research in depth aspects of adolescent
In the past several years, due to an influx of adolescent students with language and learning difficulties on my caseload, I have begun to research in depth aspects of adolescent  For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled:
For this purpose, I often use the books from the Continental Press series entitled:  Text Vocabulary Comprehension:
Text Vocabulary Comprehension: Impressions: Clinical below grade-level reading comprehension assessment reading revealed that TS presents with a number of reading related difficulties. TS’s reading fluency was marked by monotone vocal quality, awkward word stress, imprecise articulatory contacts, false-starts, self–revisions, awkward mid-sentential pauses, limited pausing for punctuation, as well as misreadings and word substitutions, all of which resulted in an impaired reading prosody. TS’s understanding as well as his verbal summary of the presented text was immature for his age and was characterized by impaired gestalt processing of information resulting in an ineffective and confusing summarization. While TS’s text-based vocabulary knowledge was deemed to be grossly adequate for his age, his reading comprehension abilities were judged to be impaired for his age. Therapeutic intervention is strongly recommended to improve TS’s reading abilities. (See Impressions and Recommendations sections for further details).
Impressions: Clinical below grade-level reading comprehension assessment reading revealed that TS presents with a number of reading related difficulties. TS’s reading fluency was marked by monotone vocal quality, awkward word stress, imprecise articulatory contacts, false-starts, self–revisions, awkward mid-sentential pauses, limited pausing for punctuation, as well as misreadings and word substitutions, all of which resulted in an impaired reading prosody. TS’s understanding as well as his verbal summary of the presented text was immature for his age and was characterized by impaired gestalt processing of information resulting in an ineffective and confusing summarization. While TS’s text-based vocabulary knowledge was deemed to be grossly adequate for his age, his reading comprehension abilities were judged to be impaired for his age. Therapeutic intervention is strongly recommended to improve TS’s reading abilities. (See Impressions and Recommendations sections for further details).