

 There are many fun language based activities parents can do at home with their newly (and not so newly) internationally adopted preschool and school aged children in the fall. One of my personal favorites is bingo. Boggles World, an online ESL teacher resource actually has a number of ready made materials, flashcards, and worksheets which can be adapted for such purposes. For example, their Fall and Halloween Bingo comes with both call out cards and a 3×3 and a 4×4 (as well as 3×3) card generator/boards. Clicking the refresh button will generate as many cards as you need, so the supply is endless! You can copy and paste the entire bingo board into a word document resize it and then print it out on reinforced paper or just laminate it.
There are many fun language based activities parents can do at home with their newly (and not so newly) internationally adopted preschool and school aged children in the fall. One of my personal favorites is bingo. Boggles World, an online ESL teacher resource actually has a number of ready made materials, flashcards, and worksheets which can be adapted for such purposes. For example, their Fall and Halloween Bingo comes with both call out cards and a 3×3 and a 4×4 (as well as 3×3) card generator/boards. Clicking the refresh button will generate as many cards as you need, so the supply is endless! You can copy and paste the entire bingo board into a word document resize it and then print it out on reinforced paper or just laminate it.
Fall vocabulary words include: corn, crops, farmer, scarecrow, apples, acorns, oak leaf, maple leaves, ginkgo leaves, grapes, mushrooms, salmon, geese, squirrel, jacket, turkey, Jack-O’-Lantern, rake, pumpkins, harvest moon, hay, chestnuts, crow, and sparrow
Halloween vocabulary words include: witch, ghost, skeleton, skull, spider, owl, Jack-O’-Lantern, devil, cobweb, graveyard, clown, pirate, robot, superhero, mummy, vampire, bat, black cat, trick or treaters, alien, werewolf
Now the fun begins!
Some suggested activities:
Practice Vocabulary Labeling: Label the words for newly adopted IA children and get them to say the words after you.
Practice Simple Sentences: Make up simple sentences such as A spider lives in a cobweb or A squirrel is eating an acorn.
Practice Rhyming: what rhymes with cat/bat/ trick/leaf/ rake/moon?
For those children who are having articulation (speech) difficulties practice saying words with select sounds (/ch/, /sh/, /l/, etc) to improve their intelligibility (pronunciation)
Practice Categorization Skills: Name some fall words, Halloween words, name some popular halloween costumes, name some popular fall activities, etc
Practice naming Associations: what goes with a witch (broom), what goes with a squirrel (acorn), etc
Practice expanding vocabulary by providing Attributes (object characteristics): Take a noun-word (thing) such as “squirrel” and answer some questions about it: what is it? what does it do? where do you find it? what are its parts? What color/shape is it? does it make any sounds? what goes with it. Here’s one example, (I see a pumpkin. It’s a fruit/vegetable that you can plant, grow and eat. You find it on a farm. It’s round and orange and is the size of a ball. Inside the pumpkin are seeds. You can carve it and make a jack o lantern out of it).
Practice expanding language by providing relevant Definitions: Tell me what a skeleton is. Tell me what a scarecrow is.
Practice improving their Problem Solving abilities by naming Similarities and Differences among semantically related items: How are pumpkin and apple alike? How are they different?
Help them understand that many words can have more than one meaning and explain Multiple Meaning words to them: A bat, witch, clown, can mean _____ and also mean _________
So join in the fun and start playing today! 
Resources:
Bogglesworld Halloween Bingo Board and Cards http://bogglesworldesl.com/halloweenbingo.htm
Bogglesworld Fall Bingo Board and Cards http://bogglesworldesl.com/autumn_bingo.htm
 Today I am excited to tell you about another product in my assessment referral series: SPEECH LANGUAGE ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST FOR PRESCHOOL CHILDREN
Today I am excited to tell you about another product in my assessment referral series: SPEECH LANGUAGE ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST FOR PRESCHOOL CHILDREN 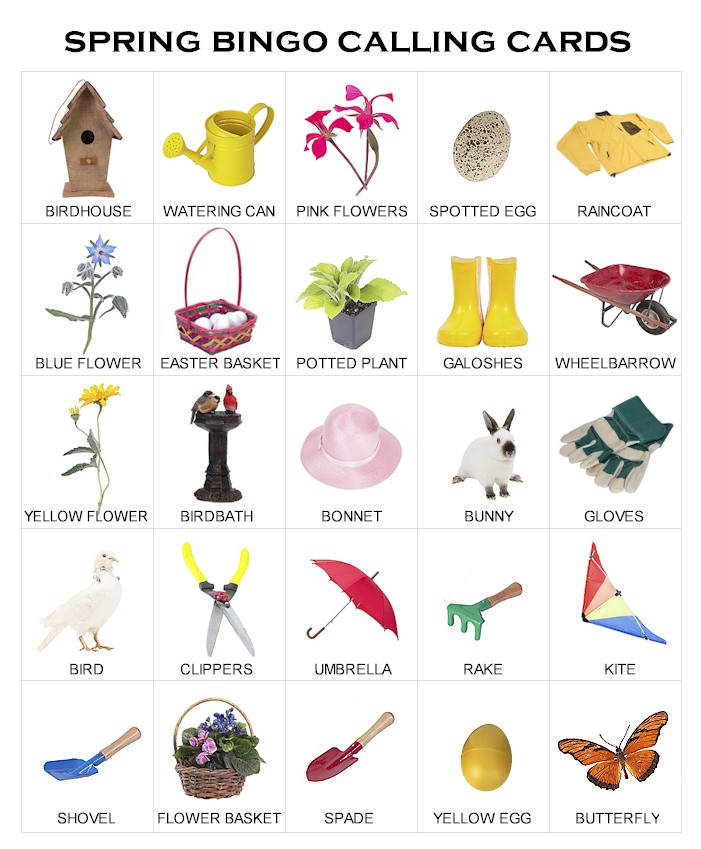 Back in late February I did a guest post for Teach Speech 365. In case you missed it I am running it again on my blog since spring is now in full bloom!
Back in late February I did a guest post for Teach Speech 365. In case you missed it I am running it again on my blog since spring is now in full bloom! Today Thanks to the generosity of Lavelle Carlson of
Today Thanks to the generosity of Lavelle Carlson of 
 This article was originally published in December 24, 2012 issue of Advance for Speech Language Pathologists and Audiologists under the title: “Adoption & Pragmatic Problems” (pp 6-9)
This article was originally published in December 24, 2012 issue of Advance for Speech Language Pathologists and Audiologists under the title: “Adoption & Pragmatic Problems” (pp 6-9) 

 There are many fun language based activities parents can do at home with their newly (and not so newly) internationally adopted preschool and school aged children in the fall. One of my personal favorites is bingo. Boggles World, an online ESL teacher resource actually has a number of ready made materials, flashcards, and worksheets which can be adapted for such purposes. For example, their
There are many fun language based activities parents can do at home with their newly (and not so newly) internationally adopted preschool and school aged children in the fall. One of my personal favorites is bingo. Boggles World, an online ESL teacher resource actually has a number of ready made materials, flashcards, and worksheets which can be adapted for such purposes. For example, their 
















 A to Z Jr– a game of early categorizations is recommended for players 5 – 10 years of age, but can be used with older children depending on their knowledge base. The object of the game is to cover all letters on your letter board by calling out words in specific categories before the timer runs out. This game can be used to
A to Z Jr– a game of early categorizations is recommended for players 5 – 10 years of age, but can be used with older children depending on their knowledge base. The object of the game is to cover all letters on your letter board by calling out words in specific categories before the timer runs out. This game can be used to  Tribond Jr – is another great game which purpose is to determine how 3 seemingly random items are related to one another. Good for older children 7-12 years of age it’s also great for problem solving and reasoning as some of the answers are not so straight forward (e.g., what do the clock, orange and circle have in common? Psst…they are all round)
Tribond Jr – is another great game which purpose is to determine how 3 seemingly random items are related to one another. Good for older children 7-12 years of age it’s also great for problem solving and reasoning as some of the answers are not so straight forward (e.g., what do the clock, orange and circle have in common? Psst…they are all round) Blurt – a game for children 10 and up is a game that works on a simple premise. Blurt out as many answers as you can in order to guess what the word is. Blurt provides ready-made definitions that you read off to players so they could start guessing what the word is. Players and teams use squares on the board strategically to advance by competing in various definition challenges that increase language opportunities.
Blurt – a game for children 10 and up is a game that works on a simple premise. Blurt out as many answers as you can in order to guess what the word is. Blurt provides ready-made definitions that you read off to players so they could start guessing what the word is. Players and teams use squares on the board strategically to advance by competing in various definition challenges that increase language opportunities. Guess Who (age 6+),
Guess Who (age 6+),  Guess Where (age 6+), and Mystery Garden (age 4+) are great for encouraging students to ask relevant questions in order to be the first to win the game. They are also terrific for encouraging reasoning skills. Questions have to be thought through carefully in order to be the first one to win the game.
Guess Where (age 6+), and Mystery Garden (age 4+) are great for encouraging students to ask relevant questions in order to be the first to win the game. They are also terrific for encouraging reasoning skills. Questions have to be thought through carefully in order to be the first one to win the game.  In 30 Second Mysteries kids need to use critical thinking and deductive reasoning in order to solve mysteriously sounding cases of everyday events. Each clue read aloud reveals more about the mystery and the trick is to solve it given the fewest number of clues in order to gain the most points.
In 30 Second Mysteries kids need to use critical thinking and deductive reasoning in order to solve mysteriously sounding cases of everyday events. Each clue read aloud reveals more about the mystery and the trick is to solve it given the fewest number of clues in order to gain the most points.


