
If someone asked me today how long I’ve been thinking about writing this post I wouldn’t hesitate and say… 3 years. I know this because that’s when I encountered my very first case of “it’s normal”. I had been in private practice for several years, when I was contacted by parents who wanted me to evaluate their 4 year old son due to concerns over his language abilities. When I first opened my office door to let them in I encountered a completely non-verbal child with significant behavioral deficits and limited communicative intent.
I have to confess, as I was conducting an extremely difficult assessment, I was very shocked by the fact that prior to seeing me, the child had not undergone any in-depth assessments with any related professionals despite presenting with pretty significant symptoms, which included: lack of meaningful interaction with toys, stereotypical behaviors (e.g., rapid flicking of his fingers in front of his eyes for extended period of time, perseverative repetitions of unintelligible sounds out of context, etc), temper tantrums, as well as complete absence of words, phrases and sentences for his age. Very tactfully I broached the subject with the parents only to find out that the parents were concerned regarding their child’s development for quite a while, only to be told by over and over again by their pediatrician that “it’s normal”. I hastily bit back my reply, before I could rudely blurt out: “in which universe?” Instead, I finished the assessment, wrote my 8 page report with extensive recommendations and referrals, and began treating the client. Luckily, since that time he had received numerous appropriate interventions from a variety of related professionals and made some nice gains. But to this day I wonder: Would his gains have been greater had his intervention was initiated at an earlier age (e.g., 2 instead of 4)?
Of course, this is by far one of the more extreme examples that I have seen during the course of my relatively short career (less than 10 years of practice) as a speech language pathologist. But I have certainly seen others.
For example, a few years ago through my hospital based job I’ve treated a child with significant unilateral facial weakness, and a host of phonation, articulation, respiration, and resonance symptoms which included: difficulty managing oral secretions, weak voice, hypernasality, dysarthric vocal quality, and a few others. Again, the parent was told by the physician that the child’s facial asymmetry and symptomology was ‘not significant’’ despite the fact that in addition to the above signs, the child also presented with significantly delayed language development, cognitive limitations and severe behavioral manifestations.
Then of course there were a few stutterers with a host of social history red flags who stuttered for a few years well into early school age, each of whose parents were told by their child’s doctor that s/he will grow out of it.

I am not even counting dozens and dozens of phone calls from concerned parents of language delayed toddlers and preschoolers whose pediatricians told them that they’ll “grow out of it” despite the fact that many of these children ended up receiving speech language services for language delays/disorders for several years afterwards.
I’ve also seen professionals without a specialization in International Adoption diagnosing recently adopted older post-institutionalized children with history of severe trauma, profound language delays, alcohol related deficits and symptoms of institutional autism as Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD).
But I don’t want you to think that I am singling out pediatricians in this post. The truth is that if we look closely we will find that this trend of overconfident recommendations is common to a vast majority of both medical and ancillary professionals (e.g., psychologists, occupational therapists, etc) with speech language pathologists not exempt from the above.
I’ve read a psychiatrist’s report, which diagnosed a child with Asperger’s based on a 15 minute conversation with the child, coupled with a brief physical examination (as documented in the child’s clinical record). At my urging (based on the child’s adaptive behavior, linguistic profile and rather superior social pragmatic functioning) the parents sought a second opinion with another psychiatrist, which revealed that the child wasn’t even on the spectrum but had a anxiety disorder, some of which symptoms mimicked Asperger’s (e.g., perseveration on topics of interest).
I’ve read numerous neurological and neuropsychological reports which diagnosed children with ADD based on the symptoms of inattention and impulsivity in select settings (e.g., school only) without a differential diagnosis to rule out language deficits, auditory processing deficits, medical conditions, or acquired syndromes such as Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders.
I’ve reviewed occupational therapy evaluations which reported on the language abilities of children vs. fine and gross motor function and sensory integration skills.
One parent even told me that when she asked a speech language therapist (who was treating her child for articulation difficulties) regarding her 10 year old son’s “ginormous” (parent’s words not mine) overbite she was told “he’ll grow into it”. I was told that the pediatric orthodontist did not appreciate that opinion and vigorously voiced his own as he was fitting the child for braces.
So when exactly did some of us decide that a differential diagnosis doesn’t matter? I’d be very curious to know what prompts professionals, who upon seeing some ‘garden variety’ symptoms, which could have a multitude of causes (e.g., inattention, echolalia, lack of speech, etc) decide that there could be only one definitive diagnosis or who merely shrug the displayed signs and accompanying parental concerns aside, expecting both to disappear on their own volition, given the passage of time.
Is it carelessness?
Is it overconfidence in own abilities?
Is it fear of losing face in front of the parent if you don’t have a ready answer?
Is it misguided belief that the child is displaying “textbook” behavior?
Is it “jadedness” or I’ve seen it all, so I know what it is, attitude?
I can venture hundreds more guesses, but it would be merely pointless speculation. Rather I prefer to focus on the intent of this post which is to outline why a differential diagnosis is so important!
1. Differential diagnosis saves lives!
Yes, I know I am only a speech pathologist and it’s true that I have yet to hear from anyone “I need a speech pathologist stat!” After all I don’t specialize in pediatric dysphagia and treat preemies in NICU.
But imagine the following scenario. A young preschool child shows up to your office with a hoarse vocal quality and a history of behavior tantrums. No problem you think, textbook vocal nodules, I got this, case closed! But what if the child was displaying additional symptoms such as stridor, coughing and difficulty breathing when sleeping? What if a few days after you’ve initiated voice therapy or told the parent that the child is too young for it, the child was rushed into the hospital because his airway was obstructed due to a laryngeal papilloma, which almost caused the child to asphyxiate. Still feel confident in your first diagnosis? Yet some speech language therapists routinely accept children into voice therapy without first referring them for an ENT consult that involves endoscopic imaging. Some of you may scoff and tell me, common, when does thing ever happen? Wouldn’t a doctor have picked up on something like that well before a child seen an SLP? Guess what … not necessarily!

Although it may be hard to believe but an EI or school-based SLP may be the first diagnostic professional many children from at-risk backgrounds come in contact with. Obstacles to receiving appropriate early medical care and ancillary services like early intervention may include limited financial means, lack of education or information, and cultural and linguistic barriers. Bilingual, multicultural, domestically adopted and foster care children from low-income households are particularly at risk since their deficits may not be detected until they begin receiving services in EI or preschool. After all, specialized medical care and related services must be sought out and paid for, which may be very hard to do for families from low SES households if they don’t have medical insurance or are having difficulty applying for Medicaid or state health insurance.
Similarly internationally adopted children are also at significant risk of despite the fact that most are adopted by middle class, financially solvent and highly educated parents. With this particular group the barriers to early identification are pre-adoption environmental risk factors (length of institutionalization and quality of medical care in that setting), combined with limited access to information (paucity of prenatal, medical and developmental history details in the adoption records).
2. Sometimes diagnosis DOES matter!
I know, I know, a number of you will try to convince me that we need to treat the symptoms and NOT the label! But humor me for a second! Let’s say you are a medical/ancillary professional (depending whom the child get’s to see first and for what reason) who gets to assess a new preschool patient/client, let’s call him Johnny. So little 4 year old Johnny walk into your office with the following symptoms:
- aggressive /inappropriate behaviors
- odd fine and gross motor movements
- clumsiness
- blunted affect (facial expression)
- inconsistent eye contact
- speech/language deficits
- picky eater with a history of stomach issues (e.g., nausea, vomiting, belly pain)
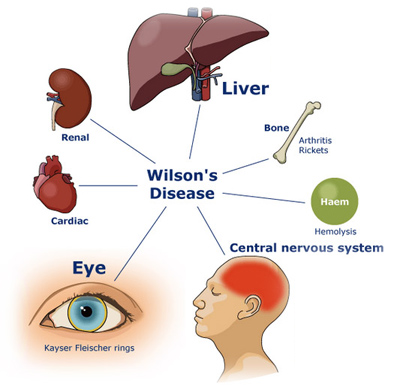
Everything you observe points to the diagnosis of Autism, after all you are the professional, and you’ve seen hundreds of such cases. It’s textbook, right? WRONG! I’ve just described to you some of the symptoms of Wilson’s disease. It’s a genetic disorder in which large amounts of copper build up in the liver and brain. This disorder has degrees of severity ranging from mild/progressive to acute/severe. It can cause brain and nervous system damage, hence the psychiatric and neuromuscular symptoms. The bad news is that this condition can be fatal if misdiagnosed/undiagnosed! The good news is that it is also VERY treatable and can be easily managed with medication, dietary changes, and of course relevant therapies (e.g, PT, OT, ST, etc)!
3. Correct Diagnosis can lead to Appropriate Treatment!
So we all know that ADHD diagnosis is currently being doled out like candy to practically every child with the symptoms of Inattention, Hyperactivity and Impulsivity. But can you actually GUESS how many children are misdiagnosed with it?
Elder (2010), found that nearly 1 million children in US are potentially misdiagnosed with ADHD simply because they are the youngest and most immature in their kindergarten class. Here’s what he has to say on the subject: “A child’s birth date relative to the eligibility cutoff … strongly influences teachers’ assessments of whether the child exhibits ADHD symptoms but is only weakly associated with similarly measured parental assessments, suggesting that many diagnoses may be driven by teachers’ perceptions of poor behavior among the youngest children in a classroom. These perceptions have long-lasting consequences: the youngest children in fifth and eighth grades are nearly twice as likely as their older classmates to regularly use stimulants prescribed to treat ADHD.” (Elder, 2010, 641)

Here are a few examples of ADHD misdiagnosis straight from my caseload.
Case A: 9 year old girl, Internationally Adopted at the age of 16 months diagnosed with ADHD based on the following symptoms:
- Inattentive
- Frequently misheard verbal messages
- Difficulty following verbal directions
- Very distractible
- Blurted things out impulsively
- Constantly forgot what had been told to her
- Made careless mistakes on school/home work
Prior to medicating the child, the parents sought a language evaluation at the advice of a private social worker. My assessment revealed a language processing disorder and a recommendation for a comprehensive APD assessment with an audiologist. Comprehensive audiological assessment revealed the diagnosis of APD with recommendations for language intervention. After language therapy with a focus on improving the child’s auditory processing skills was initiated, her symptoms improved dramatically. The recommendations for medication were scrapped.
Case B: 12 year old boy attending outpatient school in a psychiatric hospital diagnosed with ADHD and medicated unsuccessfully for it for several years based on the following symptoms:
- Severely Impulsive and Inattentive
- Occasional tantrums, opposition and aggressive behaviors
- Difficulty with transitions
- Odd Behaviors/Inappropriate Statements
- Off-topic/Unrelated Comments
- Topic Perseverations
- Poor memory
- Poor ability to follow directions
Detailed case history interview performed prior to initiation of a comprehensive language assessment revealed a history of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) at 18 months of age. Apparently the child was dropped on concrete floor head first by his biological father. However, no medical follow up took place at the time due to lack of household stability. The child was in and out of shelter with mother due to domestic abuse in the home perpetrated by biological father.
The child’s mother reported that he developed speech and language early without difficulties but experienced a significant skills regression around 1.5-2 years of age (hint, hint). Comprehensive language assessment revealed numerous language difficulties, many of which were in the areas of memory, comprehension as well as social pragmatic language. Following the language assessment, relevant medical referrals at the age of 12 substantiated the diagnosis of TBI (better late than never). So no wonder the medication had no effect!
So what can parents do to ensure that their child is being diagnosed appropriately and receives the best possible services from various health professionals?
For starters, make sure to carefully describe all the symptoms that your child presents with (write them down to keep track of them if necessary). It is important to understand that many conditions are dynamic in nature and may change symptoms over time. For example, children with alcohol related disorders may display feeding deficits as infants, delayed developmental milestones as toddlers, good conversational abilities but poor social behavior and abstract thinking skills as school aged children and low academic achievement as adolescents.
Ensure that the professional spends adequate period of time with the child prior to generating a report or rendering a diagnosis. We’ve all been in situations when reports/diagnoses were generated based on a 15 minute cursory visit, which did not involve any follow up testing or when the report was generated based on parental interview vs. actual face to face contact and interaction with the child. THIS IS NOT HOW IT’S SUPPOSED TO WORK! THIS IS HOW MISDIAGNOSES HAPPEN!
Don’t be afraid to ask follow up questions or request rationale for the professionals’ decisions. If you don’t understand something or are skeptical of the results, don’t be afraid to question the findings in a professional way. If the information provided to you seems inadequate or poorly justified consider getting a second opinion with another professional.
Make sure that your child is being treated as a unique individual and not as a textbook subject. Don’t you just hate it when you are trying to describe something to a professional and they look like they are listening but in reality they are not really ‘hearing’ you because they already “know what you have”. Or they are looking at your child but they are not really seeing him/her, because he/she is just another ‘textbook case’ in a long cue of clients. THIS IS NOT THE TREATMENT YOU ARE SUPPOSED TO GET FROM PROFESSIONALS! If this is how your child being treated then maybe it’s time to switch providers!
And another thing there are NO textbook clients! All clients are unique! I currently have about 10 post institutionalized Internationally Adopted children on my caseload with similar deficits but completely different symptom presentation, degrees of severely, as well as overall functioning. Even though some are around the same age, they are so dramatically different from one another that I need to use completely different approaches when I am planning their respective interventions.

Here’s how we as health professionals can better serve our clients/patients needs
It’s all in the details! Carefully collect the client’s background history without leaving anything out. No piece of information is too small/inconsequential! You never know what might be relevant.
Get down to the nitty gritty by asking specific questions. If you ask general questions you’ll get general responses. For example, numerous health care professionals in various fields (doctors, psychiatrists, psychologists, SLPs, etc) routinely ask biological, adoptive and foster parents and adoptive caregivers whether substance abuse of drugs/alcohol took place before and during pregnancy (that they know of with respect to the latter two). A number will respond that yes it took place during pregnancy but stopped as soon as the mother found out she was pregnant. Many professionals will leave it at that and move on to the next line of questioning. However, the follow up question to the above response should always be: “How many months along was the biological mother when she found out she was pregnant?” You’d be surprised at the responses you’ll get, which may significantly clarify the “mystery” of the child’s current symptomology.
Pretend that each new case is your very first case! Remember how you were fresh out of grad school/residency? How much enthusiasm, time, and effort you’ve put in leaving no stone unturned to diagnose your clients? That’s the passion and dedication the parents are looking for.
It’s always fun to play a detective! How cool was “House” when it first came out? House and his team left no stone unturned in trying to correctly diagnose their patients. At times they even went to their houses or places of work in order to find any shred of information that would lead them on the right path. Admittedly you don’t have to go quite that far, but a consultation with a related professional might do the trick if a client is exhibiting certain symptoms outside your experience.

Turn your weakness into strength! No one likes to admit that they don’t have the answer. Many of us worry that our clients (those who work with adults) or their parents (those who work with children) may lose confidence in us and go elsewhere for services. But everything depends on how you frame it! If you simply explain to the parent the rationale for the referral and why you want them to see another specialist prior to formulating the final diagnosis, they will only THANK YOU! It will show them that rather than making a casual decision, you want to make the best decision in their child’s case and they will only appreciate your candor as to them it shows your commitment to the care of their child.
It doesn’t matter how well educated and well trained many medical and related professionals are, the fact remains – no one knows everything! That is why each of us has our own unique scope of practice! That is why we should operate within our scope of practice and referral clients for additional assessments when needed. Differential diagnosis should not be an exception; it should be a rule for any patient who does not show ‘unique’ symptoms indicative of very specific disorders/conditions! It should be performed with far greater frequency than it is done right now by medical and related health professionals!
After all: “When you have excluded all possibilities, then what remains -however improbable – must be the truth”. ~Sherlock Holmes
References:
- Elder, T (2010). The Importance of Relative Standards in ADHD Diagnoses: Evidence Based on a Child’s Date of Birth, Journal of Health Economics, 29(5): 641-656.
- Zacharisen, M & Conley, S (2006) Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis in Children: Masquerader of Common Respiratory Diseases. Pediatrics 118 (5): 1925-1931.
- Gow P, Smallwood R, Angus P, Smith A, Wall A, Sewell R. (2000) Diagnosis of Wilson’s disease: an experience over three decades. GUT: International Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 46: 415–419.


 For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the
For that purpose, Len is a good candidate for the administration of the  Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the
Given Len’s reported history of narrative production deficits, Len is also a good candidate for the administration of the 



 The Test of Silent Word Reading Fluency (TOSWRF-2)
The Test of Silent Word Reading Fluency (TOSWRF-2) 






 Lately, I’ve been seeing more and more posts on social media asking for testing suggestions for students who exhibit
Lately, I’ve been seeing more and more posts on social media asking for testing suggestions for students who exhibit 
 It’s early August, and that means that the start of a new school year is just around the corner. It also means that many newly graduated clinical fellows (as well as SLPs switching their settings) will begin their exciting yet slightly terrifying new jobs working for various school systems around the country. Since I was recently interviewing clinical fellows myself in my setting (an outpatient school located in a psychiatric hospital, run by a university), I decided to write this post in order to assist new graduates, and setting-switching professionals by describing what knowledge and skills are desirable to possess when working in the schools.
It’s early August, and that means that the start of a new school year is just around the corner. It also means that many newly graduated clinical fellows (as well as SLPs switching their settings) will begin their exciting yet slightly terrifying new jobs working for various school systems around the country. Since I was recently interviewing clinical fellows myself in my setting (an outpatient school located in a psychiatric hospital, run by a university), I decided to write this post in order to assist new graduates, and setting-switching professionals by describing what knowledge and skills are desirable to possess when working in the schools. 
 The following is an informational post on the disease SMA (spinal muscle atrophy) by Rose Ann Kesting M.A. CCC-SLP. After reading, please
The following is an informational post on the disease SMA (spinal muscle atrophy) by Rose Ann Kesting M.A. CCC-SLP. After reading, please 